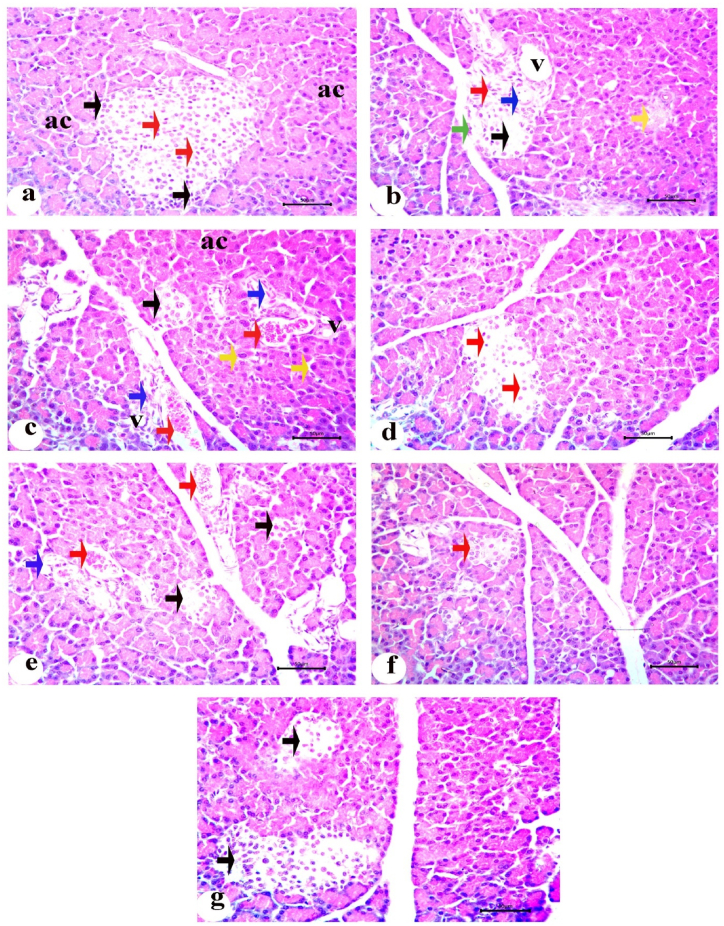
Fig. 6.
Photomicrographs of the pancreatic sections stained with H&E. a) The control group (C) showing normal pancreatic acini (ac), islet of Langerhans contains alpha cells on the peripheral side with dark, small peripheral nuclei (black arrows) and cords of β-cells with light and large nuclei (red arrows); b) Untreated diabetic group (D) revealing islets of Langerhans with cytoplasmic vacuolation (V), degeneration (black arrow), pyknosis (red arrow), necrosis of β-cells (blue arrow) and mitotic figure (green arrow). There are completely shrunken and degenerated islet (yellow arrow); c) Another pancreatic section of diabetic group (D) revealed karyomegaly of acinar cells (yellow arrows), apoptosis (blue arrows) and small shrunken islet (black arrow) in addition to congestion (red arrows); d) Pancreatic section of treated group orally with INS-CsNBs-PD shell (F) displaying islet with regeneration of small number of β-cells and improving of degenerative changes (red arrows); e) Pancreatic section from the diabetic group treated with free insulin via oral administration (FO) presenting shrinkage in islets with degeneration (black arrows), congestion (red arrows) and cytoplasmic vacuolation (blue arrow); f) Pancreatic section of diabetic group treated orally with CsNBs-PD shell (NB) showing small islet without degenerative effect of these nanoparticles (red arrow); g.) The section of treated group injected with subcutaneous insulin (Sc) exhibiting of islets with ameliorative effect and regeneration of β-cells with considerable rise in islet volume (black arrows). (Scale bar = 50 μm) (n = 6). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)