Abstract
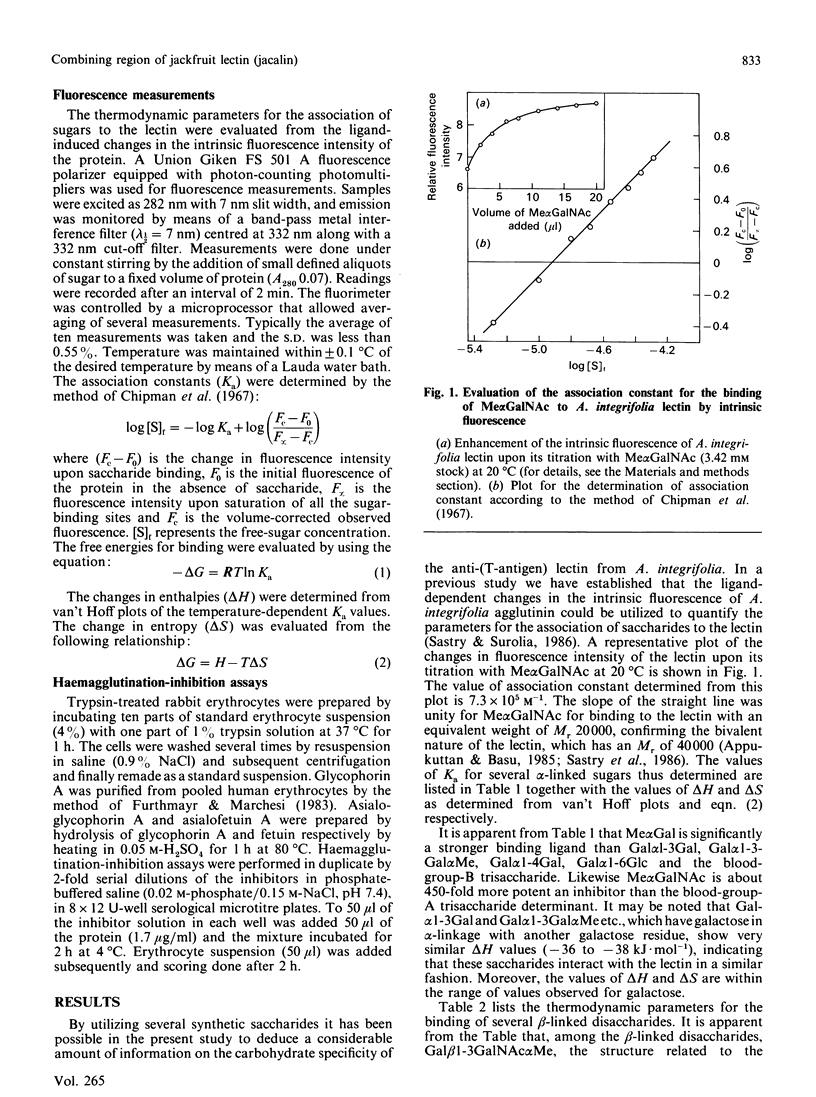
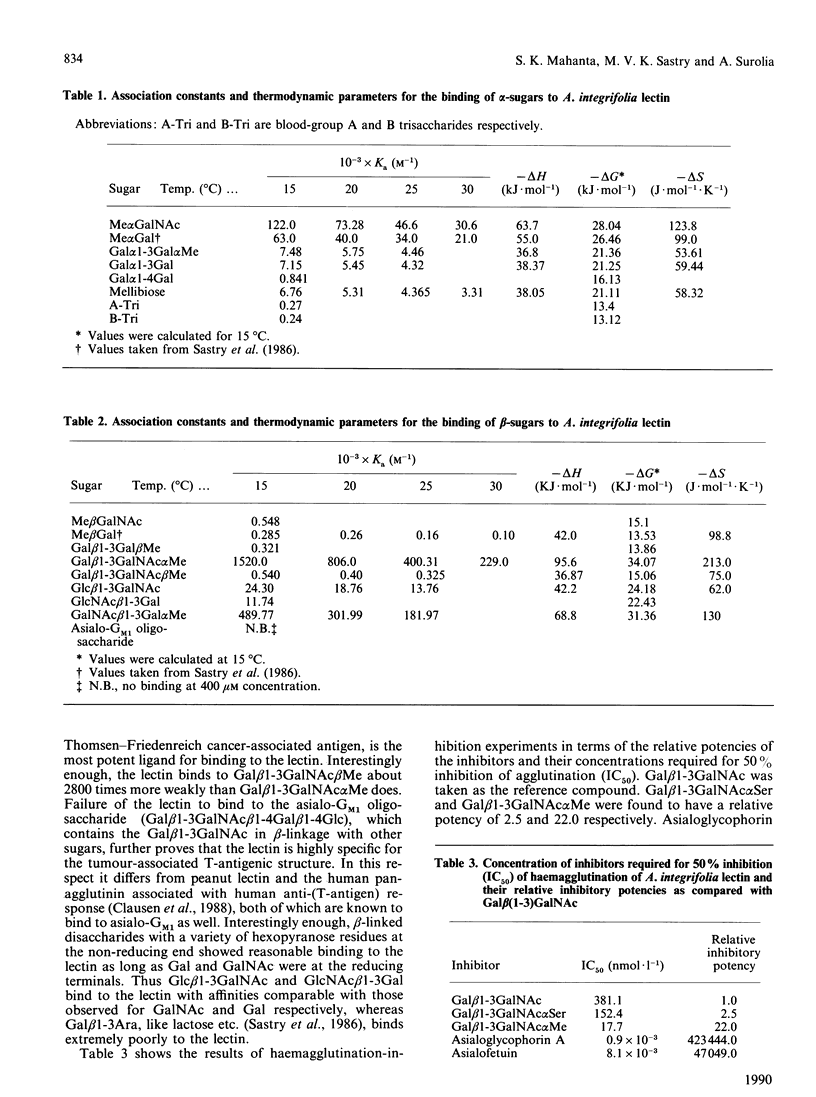
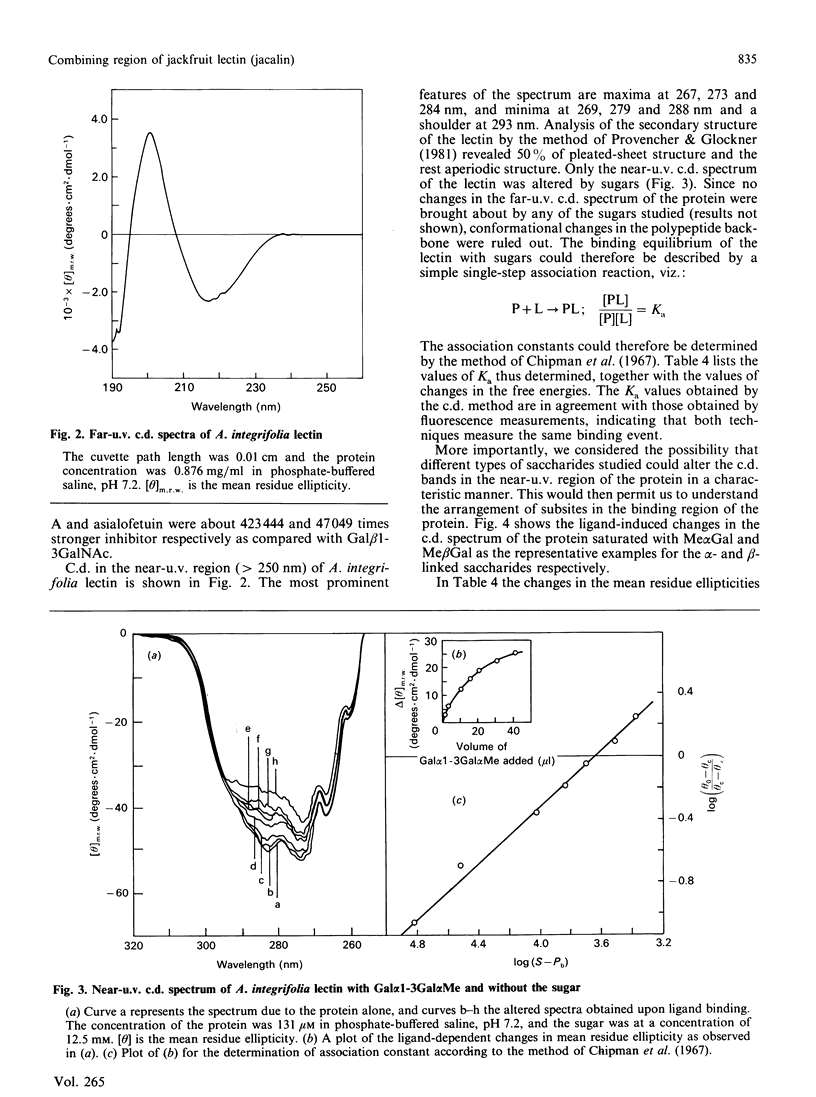
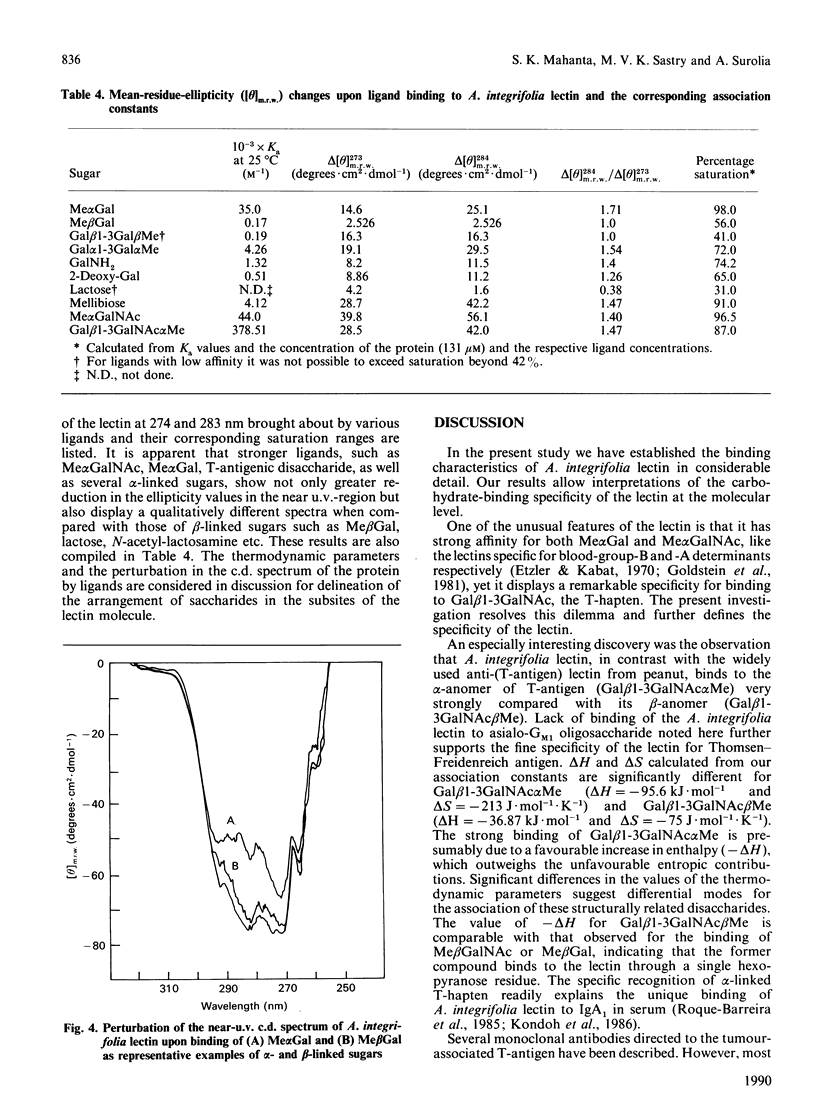
Thermodynamic analysis of carbohydrate binding by Artocarpus integrifolia (jackfruit) agglutinin (jacalin) shows that, among monosaccharides, Me alpha GalNAc (methyl-alpha-N-acetylgalactosamine) is the strongest binding ligand. Despite its strong affinity for Me alpha GalNAc and Me alpha Gal, the lectin binds very poorly when Gal and GalNAc are in alpha-linkage with other sugars such as in A- and B-blood-group trisaccharides, Gal alpha 1-3Gal and Gal alpha 1-4Gal. These binding properties are explained by considering the thermodynamic parameters in conjunction with the minimum energy conformations of these sugars. It binds to Gal beta 1-3GalNAc alpha Me with 2800-fold stronger affinity over Gal beta 1-3GalNAc beta Me. It does not bind to asialo-GM1 (monosialoganglioside) oligosaccharide. Moreover, it binds to Gal beta 1-3GalNAc alpha Ser, the authentic T (Thomsen-Friedenreich)-antigen, with about 2.5-fold greater affinity as compared with Gal beta 1-3GalNAc. Asialoglycophorin A was found to be about 169,333 times stronger an inhibitor than Gal beta 1-3GalNAc. The present study thus reveals the exquisite specificity of A. integrifolia lectin for the T-antigen. Appreciable binding of disaccharides Glc beta 1-3GalNAc and GlcNAc beta 1-3Gal and the very poor binding of beta-linked disaccharides, which instead of Gal and GalNAc contain other sugars at the reducing end, underscore the important contribution made by Gal and GalNAc at the reducing end for recognition by the lectin. The ligand-structure-dependent alterations of the c.d. spectrum in the tertiary structural region of the protein allows the placement of various sugar units in the combining region of the lectin. These studies suggest that the primary subsite (subsite A) can accommodate only Gal or GalNAc or alpha-linked Gal or GalNAc, whereas the secondary subsite (subsite B) can associate either with GalNAc beta Me or Gal beta Me. Considering these factors a likely arrangement for various disaccharides in the binding site of the lectin is proposed. Its exquisite specificity for the authentic T-antigen, Gal beta 1-3GalNAc alpha Ser, together with its virtual non-binding to A- and B-blood-group antigens, Gal beta 1-3GalNAc beta Me and asialo-GM1 should make A. integrifolia lectin a valuable probe for monitoring the expression of T-antigen on cell surfaces.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anglin J. H., Jr, Lerner M. P., Nordquist R. E. Blood group-like activity released by human mammary carcinoma cells in culture. Nature. 1977 Sep 15;269(5625):254–255. doi: 10.1038/269254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appukuttan P. S., Surolia A., Bachawat B. K. Isolation of two galactose-binding proteins from Ricinus communis by affinity chromatography. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1977 Dec;14(4):382–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu D., Delucas L., Parks E. H., Suddath F. L. Preliminary crystallographic study of the alpha-D-galactose-specific lectin from jack fruit (Artocarpus integra) seeds. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):661–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90646-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K., Breimer M. E., Brignole A., Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., Leffler H., Samuelsson B. E., Strömberg N., Edén C. S. Specificity of binding of a strain of uropathogenic Escherichia coli to Gal alpha 1----4Gal-containing glycosphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8545–8551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn-Moreno M. M., Campos-Neto A. Lectin(s) extracted from seeds of Artocarpus integrifolia (jackfruit): potent and selective stimulator(s) of distinct human T and B cell functions. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):427–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipman D. M., Grisaro V., Sharon N. The binding of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to lysozyme. The specificity of binding subsites. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4388–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen H., Levery S. B., Kannagi R., Hakomori S. Novel blood group H glycolipid antigens exclusively expressed in blood group A and AB erythrocytes (type 3 chain H). I. Isolation and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1380–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen H., Stroud M., Parker J., Springer G., Hakomori S. Monoclonal antibodies directed to the blood group A associated structure, galactosyl-A: specificity and relation to the Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen. Mol Immunol. 1988 Feb;25(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. F., Goldstein I. J., Arnarp J., Lönngren J. Carbohydrate binding studies on the lectin from Datura stramonium seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):524–533. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanaraj V., Patanjali S. R., Surolia A., Vijayan M. Preparation and preliminary X-ray studies of two crystal forms of the anti-T lectin from jackfruit (Artocarpus integrifolia) J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):1135–1136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzler M. E., Kabat E. A. Purification and characterization of a lectin (plant hemagglutinin) with blood group A specificity from Dolichos biflorus. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):869–877. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Glycophorins: isolation, orientation, and localization of specific domains. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:268–280. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Blake D. A., Ebisu S., Williams T. J., Murphy L. A. Carbohydrate binding studies on the Bandeiraea simplicifolia I isolectins. Lectins which are mono-, di-, tri-, and tetravalent for N-acetyl-D-galactosamine. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3890–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Kobayashi K., Hagiwara K., Kajii T. Jacalin, a jackfruit lectin, precipitates IgA1 but not IgA2 subclass on gel diffusion reaction. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 17;88(2):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna Sastry M. V., Swamy M. J., Surolia A. Analysis of dynamics and mechanism of ligand binding to Artocarpus integrifolia agglutinin. A 13C and 19F NMR study. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14826–14831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronis K. A., Carver J. P. Specificity of isolectins of wheat germ agglutinin for sialyloligosaccharides: a 360-MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance binding study. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3050–3057. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald D. L., Patt L. M., Hakomori S. Notes on improved procedures for the chemical modification and degradation of glycosphingolipids. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):642–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurohr K. J., Bundle D. R., Young N. M., Mantsch H. H. Binding of disaccharides by peanut agglutinin as studied by ultraviolet difference spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):305–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurohr K. J., Young N. M., Mantsch H. H. Determination of the carbohydrate-binding properties of peanut agglutinin by ultraviolet difference spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9205–9209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kabat E. A., Lotan R., Sharon N. Immunochemical studies on the specificity of the peanut (Arachis hypogaea) agglutinin. Carbohydr Res. 1976 Oct;51(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kisailus E. C., Gruezo F., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on the combining site of the blood group H-specific lectin 1 from Ulex europeus seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C., Preston J. M. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of soybean lectin-monosaccharide interactions: computer analysis of complex binding behavior. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 15;247(1):190–200. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roque-Barreira M. C., Campos-Neto A. Jacalin: an IgA-binding lectin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1740–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roque-Barreira M. C., Praz F., Halbwachs-Mecarelli L., Greene L. J., Campos-Neto A. IgA-affinity purification and characterization of the lectin jacalin. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1986;19(2):149–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry M. V., Banarjee P., Patanjali S. R., Swamy M. J., Swarnalatha G. V., Surolia A. Analysis of saccharide binding to Artocarpus integrifolia lectin reveals specific recognition of T-antigen (beta-D-Gal(1----3)D-GalNAc). J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11726–11733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry M. V., Surolia A. Intrinsic fluorescence studies on saccharide binding to Artocarpus integrifolia lectin. Biosci Rep. 1986 Oct;6(10):853–860. doi: 10.1007/BF01116238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Bhoyroo V. D. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5704–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on fetuin, a glycoprotein of fetal serum. I. Isolation, chemical composition, and physiochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235(10):2860–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Desai P. R., Murthy M. S., Tegtmeyer H., Scanlon E. F. Human carcinoma-associated precursor antigens of the blood group MN system and the host's immune responses to them. Prog Allergy. 1979;26:42–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson G., Albertsson J., Svensson C., Magnusson G., Dahmén J. X-ray crystal structure of galabiose, O-alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-(1---4)-D-galactopyranose. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Jan 15;146(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(86)85021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


