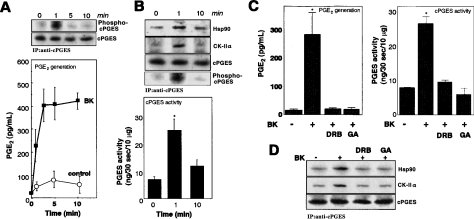
Figure 4. Bradykinin (BK)-induced phosphorylation and activation of cPGES.
(A) Time course of PGE2 production after incubation for the indicated periods with or without 10 μM BK (lower panel). Results are means±S.D. for four independent experiments. 32P-incorporation into cPGES (Phospho-cPGES) at each time point was assessed by immunoprecipitation and subsequent autoradiography, and equal precipitation of cPGES protein from each sample was verified by immunoblotting (upper panel). (B) Formation of the cPGES–CK-II–Hsp90 complex and cPGES phosphorylation after stimulation with BK for indicated periods were assessed by the immunoprecipitation (IP) assay (upper panel). PGES activity in cell lysates at each time point was measured (lower panel). Results are means±S.D. for seven independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with experiments without BK stimulation). (C) Effects of DRB and geldanamycin (GA) on PGE2 production (left-hand panel) and cPGES enzymic activity in cell lysates (right-hand panel). Cells were pre-incubated for 5 h with these agents and then treated for 1 min with (+) or without (−) BK. Results are means±S.D. for four independent experiments (*P<0.05 compared with BK stimulation without inhibitors). (D) Effects of DRB and GA on the formation of the cPGES–CK-II–Hsp90 complex, as determined by immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblotting. A blot representative of five independent experiments is shown.