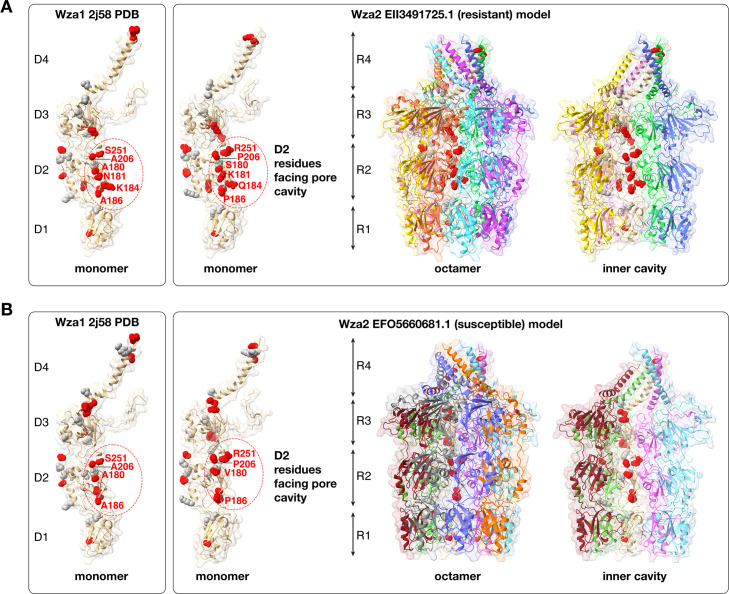
Fig 7.
Changes between Wza1 (crystal structure 2j58) and Wza2 mapped on a model of the monomer and the octamer of a representative resistant (panel A) and susceptible (panel B) Wza2, distinguished by conservative (gray) vs non-conservative (red) mutations. A conservative mutation is considered one that does not dramatically change the biochemical properties of the residue (e.g., L to I or R to K) and the opposite for non-conservative (e.g., D to R). Within the R2 ring (D2 domain of the monomer), there are six non-conservative mutations at positions facing the inner pore cavity, and on the outer “lip” within the R4 ring, there are two mutations in the D4 domain from basic residues to asparagines (N).