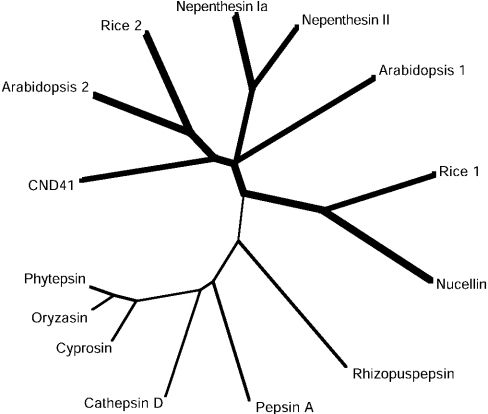
Figure 12. A phylogenetic tree for nepenthesins and related typical APs.
Bold line, the branches of the NAPs; thin line, the ordinary pepsin-type APs. The phylogenetic tree was produced by ClustalW using the sequence of residues 95–434 of prepro-nepenthesin Ia and the corresponding sequences of the other APs, after removing the NAP-specific insertion and the plant-specific insertion. The sequences of the following 12 APs are compared: (1) nepenthesin Ia, N. gracilis AP Ia (AB114914); (2) nepenthesin II, N. gracilis AP II (AB114915); (3) Arabidopsis 1, A. thaliana AP (AF37029) (Ip, 4.3); (4) Arabidopsis 2, A. thaliana AP (AY088536) (Ip, 9.5); (5) nucellin, H. vulgare (barley) AP (U87148); (6) rice 1, O. sativa AP (AK068348) (Ip, 8.7); (7) rice 2, O. sativa AP (AK165097) (Ip, 5.3); (8) CND41, N. tabacum (tobacco) AP (D26015); (9) cyprosin, Cynara caldunclus AP (X81984); (10) oryzasin, O. sative AP (D32114); (11) phytepsin, H. vulgare (barley) AP (X56136); (12) cathepsin D, porcine cathepsin D (M11233); (13) pepsin A, porcine pepsin A (M20920); and (14) Rhisopuspepsin, Rhizopus chinensis AP (P06026). The number in parenthesis is the accession number.