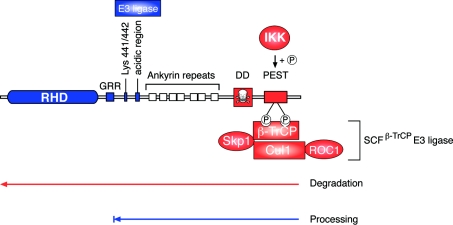
Figure 5. Proteolysis of NF-κB1 p105.
NF-κB1 p50 is constitutively produced from p105 by proteolytic removal of the C-terminal half of p105 by the proteasome (a mechanism termed processing). The GRR acts as a stop signal, preventing entry of the RHD into the proteasome, which is thought to degrade p105 from the C-terminus. The stability of the folded RHD is important in preventing its entry into the proteasome and proteolysis. The identity of the E3 ligase involved in p105 processing is not known, but has been proposed to bind to an acidic region adjacent to the ankyrin repeats. Following agonist stimulation, p105 is phosphorylated by the IKK complex on Ser927 and Ser932 in the p105 PEST region. These phosphorylated residues act a binding site for βTrCP, the recognition subunit of a multisubunit SCF-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, which catalyses the polyubiquitination of phospho-p105 on multiple lysine residues, triggering its subsequent complete degradation by the proteasome. ROC1 is a RING finger protein. Elements involved in processing are shown in blue. Elements involved in degradation are shown in red.