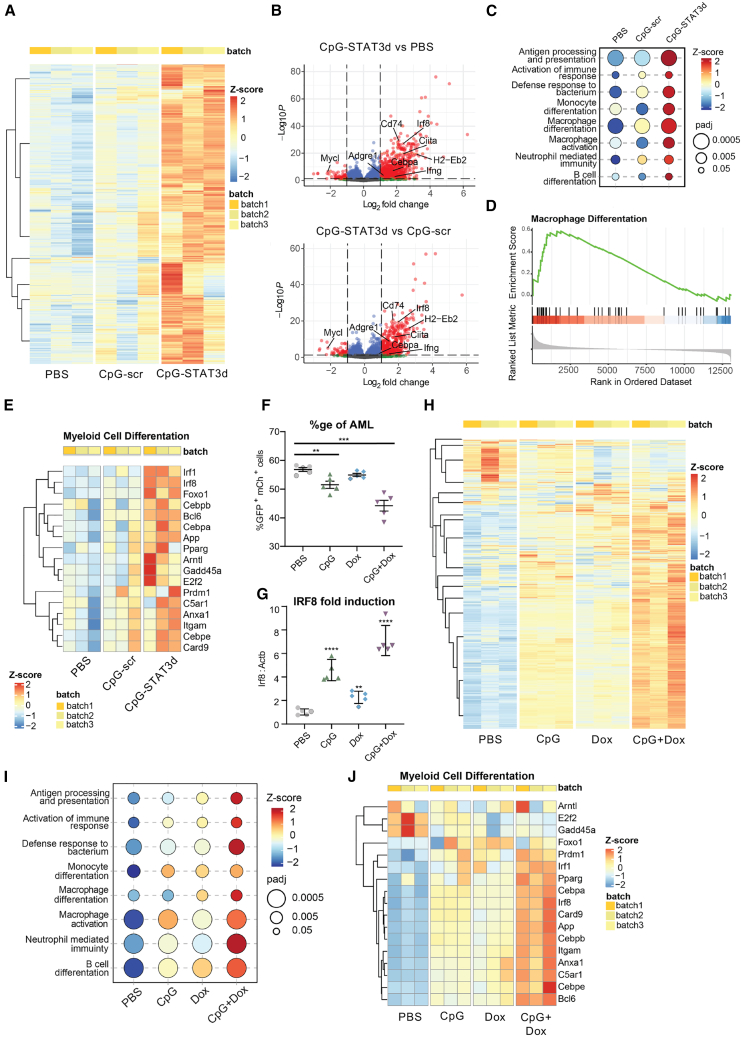
Figure 2.
The combination of STAT3 inhibition and TLR9 stimulation is required to transcriptionally reprogram CMM leukemic cells toward myeloid cell differentiation and antigen presentation
(A–D) CMM-bearing mice were treated i.v. using CpG-STAT3d or control CpG-scr oligonucleotides (5 mg/kg) every other day for three times as in Figure 1A. RNA-seq analysis was performed using magnetically enriched leukemic cells. (A) The heatmap of hierarchical clustering of differentially expressed genes (DEGs), demonstrating distinct separation between treatment groups. (B) Volcano plots of DEGs with a log2 fold change (log2FC) greater than 2 and an adjusted p value (padj) less than 0.05 shown in red, highlighting a significant majority of upregulated genes following CpG-STAT3d treatment compared with both CpG-scr and PBS treatments. (C–E) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the KEGG database-derived gene sets indicating the top-scoring immune signaling pathways for all three treatment groups (C), the gene enrichment score indicating the differentiation of AML cells primarily into macrophage-like cells (D), and the heatmap (E) of key myeloid cell differentiation gene expression in all three treatment groups. (F–J) Mice engrafted with 1 × 106 CMM-tetON-shStat3 cells expressing doxycycline-inducible STAT3shRNA (tetON-shStat3) were treated daily for six times with PBS, CpG, Dox (100 mg/kg), or CpG plus Dox. Compared with CpG or Dox treatments alone, the combined CpG/Dox treatment was the most effective in reducing splenic GFP+/mCherry+ AML cells (F) and in the upregulation of Irf8 expression in leukemic cells (G) as assessed using flow cytometry or qPCR, respectively. (H) RNA-seq analysis and hierarchical clustering showing pattern of gene expression in CMM-tetON-shStat3 cells treated with CpG+Dox as observed in the parental CMM treated with CpG-STAT3d (see A). (I and J) GSEA results (I) along with (J) a heatmap of differentially expressed genes associated with myeloid cell differentiation most robustly activated by the combined CpG+Dox treatment. All the presented data are representative of the results obtained in two independent experiments, n = 3–5 mice/group, and the quantification results were shown as means ± SEM. Statistically significant differences are indicated by asterisks: ∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001; ∗∗, p < 0.01.