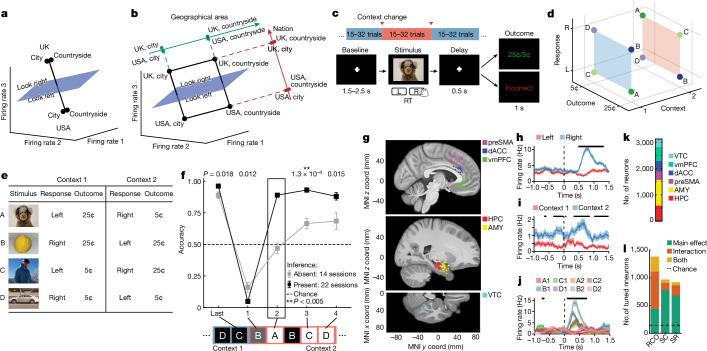
Fig. 1. Task, behaviour and single-neuron tuning.
a,b, Possible definitions of abstraction as clustering (a) or generalization (b). In the latter, the two variables are orthogonal to each other and preserved, whereas one of the variables (geographic area) is discarded in the former. c, Task and example trial. Blocks of trials alternated between the two contexts. In each trial, the stimulus remained on the screen until participants pressed a button, followed by the outcome. d,e, Task structure. d, Each stimulus (A–D) is associated with a single correct response and results in either a high or low reward if the correct response is given. e, Stimulus–response relationships are inverted between contexts 1 and 2. f, Behaviour. Accuracy is shown separately for inference present (n = 22) and absent (n = 14) sessions for the last trial before the context switch, the first trial after the context switch and for the remaining three inference trials averaged over all trials in each session (mean ± s.e.m. across sessions). The dashed line marks chance. The black box indicates inference trial 1. **P < 0.005 for rank-sum inference sbsent versus present over sessions. g, Electrode locations. Each dot denotes a microwire bundle. Locations are shown on the same hemisphere (right) for visualization purposes only. h–j, Example neurons that encode response (h), context (i) and mixtures of stimulus ID (indicated by A–D) and context (indicated by 1 or 2) (j). Error bars are ± s.e.m. across trials. t = 0 is stimulus onset. Black points indicate P < 0.05 of one-way ANOVA of plotted variables. k, Number of units recorded in each brain area. l, Number of single units across all brain areas showing significant main or interaction effects to at least one variable (n-way ANOVA, P < 0.05, Methods). Variables tested: response (R), context (C), outcome (O), and stimulus ID (S). Brain areas assessed: amygdala (AMY), dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), hippocampu (HPC), presupplementary motor area (preSMA), and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC).