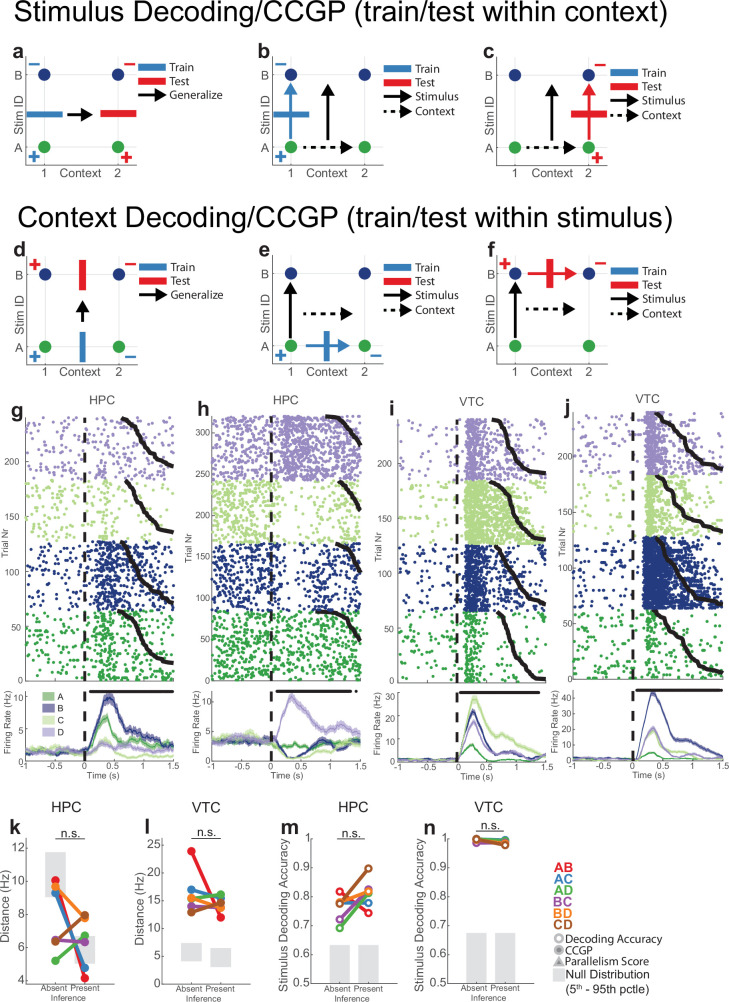
Extended Data Fig. 6. Cross-condition generalization performance for stimulus identity and context defined over stimulus pairs.
(a-f) Illustration of analysis over pairs of stimuli. When considering a pair of stimuli (e.g. A and B) across two contexts (e.g. 1 and 2), there are four possible task conditions (A1, B1, A2, B2). On these points, stimulus (A1A2 vs B1B2) and context (A1B1 vs A2B2) can be decoded in a straightforward manner, but is not informative about the format in which stimulus and context are encoded. Rather, the CCGP for stimulus across contexts (a-c) and for context across stimuli (d-f) provide information about the structure of the two variables and how they interact. (a-c) Illustration of CCGP for assessing whether stimuli are abstract with respect to context. (a) A linear decoder (blue bar) is trained to distinguish between stimuli A and B in context 1 (blue + and – correspond to class labels for training). The decoder is then tested (generalized) on context 2, where stimulus identity is decoded (red bar, + and – for class labels). (b) The training step. (c) The testing step. Arrows show the stimulus and context coding vectors. (d-f) Illustration of CCGP for assessing whether context is abstract with respect to stimulus identity. See (a-c) for notation. (g-j) Example neurons from hippocampus (g,h) and VTC (i,j) with tuning for stimulus identity. Plotting conventions identical to those used in Extended Data Fig. 1j. (k-l) Distances between pairs of stimulus representations in hippocampus (k) and VTPC (l). Color code indicates stimulus pair. Distance is the Euclidean distance between the stimulus centroids, each of which is an N (# of neurons) dimensional vector of average firing rates during stimulus presentation. Neuron counts are balanced between inference absent and inference present sessions. Null distributions are geometric nulls. Significance of the difference is tested by two-sided ranksum test computed over stimulus pairs, and n.s. indicates p > 0.01. pRS = 0.39, pRS = 0.40, pRS = 0.13, and pRS = 0.026 for panels (k-l), respectively. (m-n) Decodability of stimulus identity for hippocampus (m) and VTC (n). Each datapoint is a binary decoder between the two stimulus identities in a given pair. Significance of the difference between inference absent and inference present decodability is also established by Ranksum test over average decoding accuracies and n.s. indicates p > 0.05.