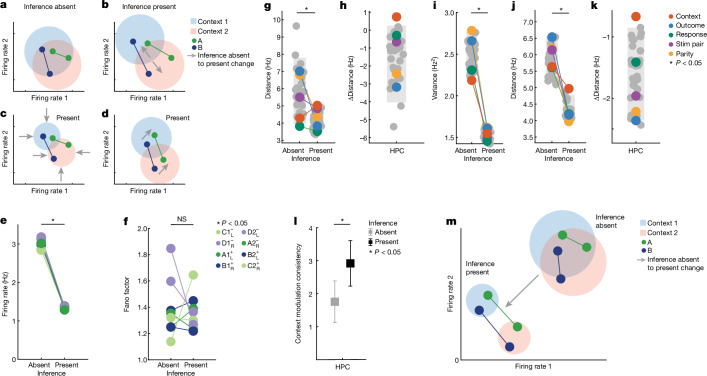
Fig. 4. Firing-rate properties underlying the emergence of abstract variables in the hippocampus.
a–d, Changes that could give rise to abstract variables. Shaded circles represent variability, and grey arrows signify changes between inference absent and present. a, Original, when variable is not abstract. b, Increase in distance. c, Decrease in variance. d, Increase in parallelism. e, Firing rates of hippocampal neurons during stimulus period decreased (PRS = 8.3 × 10−5, two-sided rank-sum over conditions). Colour indicates task state, with coding indicating identity (for example, task condition C1−L describes stimulus C, context 1, outcome , response L). f, Fano factor was not significantly different between inference present and absent sessions (two-sided rank-sum test, PRS = 0.99). g, Population distance between centroids for all 35 balanced dichotomies. Average distances decrease from inference absent to present (PRS = 2.9 × 10−8, rank-sum over dichotomies). Grey bars indicate the 5th–95th percentile of the geometric null distribution. h, Context alone is the only dichotomy whose distance significantly increases from inference absent to present (red, PΔDist = 0.040, against geometric null of difference). HPC, hippocampus. i, Average trial-by-trial variance projected along the coding direction decreased on average between inference absent and inference present sessions (PRS = 6.5 × 10−13, rank-sum test). j,k, Same as g,h, but for spike counts during the baseline period. Trials are grouped by identify the previous trial. Distance was significantly reduced across all dichotomies (j, PRS = 6.4 × 10−13, rank-sum over dichotomies) and context alone shows a distance reduction that is smaller than would be expected by chance (k, red, PΔDist = 0.027, against geometric null of difference). l, Stimulus-tuned neurons in the hippocampus were modulated by context more consistently in inference present sessions (PRS = 0.0039) during the stimulus period (n = 63, error bars are ±s.e.m. across neurons). m, Illustration of changes in neural state space. Context dichotomy distance increased, variance decreased and consistency of stimulus modulation across contexts increased. In all panels, PRS values are from a two-sided rank-sum test and grey bars indicate the 5th–95th percentile of the geometric null distribution.