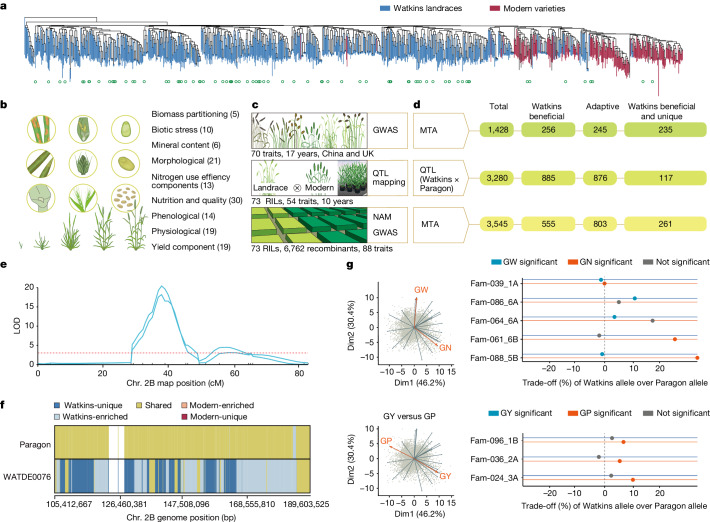
Fig. 2. Genetic dissection of useful traits from Watkins.
a, SNP phylogeny of Watkins and modern lines. The tree was built on the core SNP set (Watkins parents of 73 RIL populations are marked with green circles). b, Schematic of trait data collected and categorized into nine classes. Total number of sub-traits for each trait is shown in parentheses. c, Field experiments and trait data collected from the Watkins natural population for GWAS analysis (top), QTL analysis from individual segregating mapping populations (RIL; middle) and combined analysis of NAM–GWAS with RILs from imputation of the NAM populations (bottom). d, Genetic association signals from different methods. Total number of MTAs detected from GWAS (top), NAM (bottom). Middle, summary of total number of QTLs identified using RILs. Watkins beneficial, number of allelic effects in which the Watkins allele exceeded Paragon allele for traits under directional selection; adaptive, effects that can be beneficial in either direction; Watkins beneficial, adaptive and unique, haplotype under the peak marker or genomic interval was absent or infrequent in modern. e, Examples of genetic effect detection as QTL (yellow rust resistance) using data collected from experiments in c. LOD, logarithm of the odds. f, Haplotype frequency within QTL peak interval blocks in e for Paragon and WATDE0076 (Supplementary Table 17), as Watkins-unique, Watkins-enriched, shared, modern-enriched, modern-unique and other (white, no haploblock). g, Left, principal component analysis (PCA) of Watkins NIL data, highlighting trait trade-off relationships (grain weight (GW) versus grain number (GN) and grain yield (GY) versus grain protein (GP)). Right, percentage phenotypic differences for the Watkins versus Paragon allele. Each QTL is represented by a NIL pair or family (Fam) (Supplementary Table 31). Significant effects (P < 0.05, F-statistics) for traits are shown by coloured or grey circles.