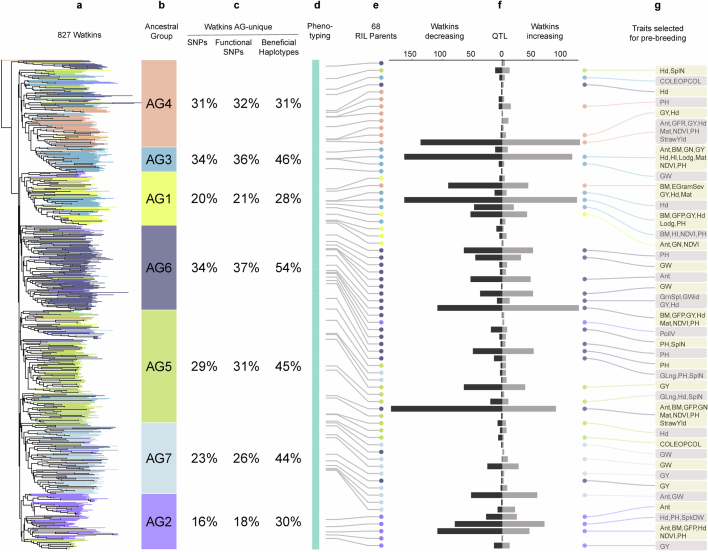
Extended Data Fig. 5. Information flow from novel and functional genetic diversity derived from Watkins landraces to the quantification of the beneficial increasing QTL allele associated with target traits.
a, Phylogenetic tree of the 827 Watkins accessions, colour-coded by ancestral groups; the branches were roughly classified into the seven ancestral groups in panel b. c, Percentage of AG-unique genetic diversity for SNPs, functional SNPs (defined by SnpEff (v4.3t)20) and beneficial haplotypes. d, Phenotyping of the Watkins collection including data collected in China and the UK and data for the 68 of 73 total RIL populations which exhibit significant QTLs in panel e. The Watkins parental lines in the RIL population, with colours representing their ancestral groups. f, distribution of the number statistic of QTLs detected from the biparental QTL mapping populations, comparison was made for the beneficial QTL with increasing effects (right) and decreasing (left) in Watkins. g, Prioritised QTL and the major traits selected for introgression into Paragon via backcrossing to test their phenotypic effects for pre-breeding.