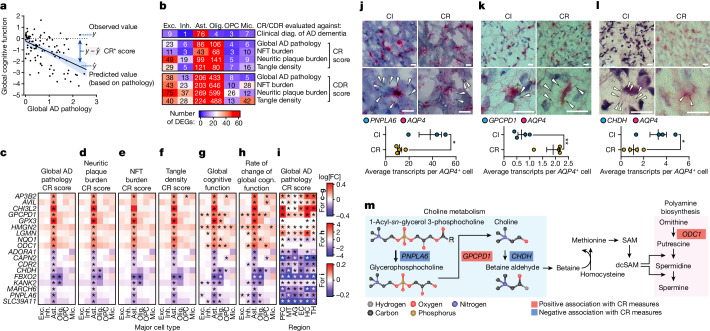
Fig. 5. Molecular correlates of CR to AD pathology.
a, The concept of CR and CDR scores. Pathology measurements are used to predict global cognitive function, for CR scores, or rate of cognitive decline, for CDR scores. b, The number of significant DEGs in major cell types across nine measures of CR. c–h, Association of astrocyte CR genes with measures of CR (global AD pathology CR score (c), neuritic plaque burden CR score (d), NFT burden CR score (e), tangle density CR score (f), global cognitive (cogn.) function (g) and rate of change of global cognitive function (h)) across six major cell types in the PFC (427 individuals, DEGs were computed using muscat). i, The association between the expression of CR genes in astrocytes across six brain regions and CR to global AD pathology (48 individuals; DEGs were computed using MAST). j–l, RNAscope validation of the differentially expressed astrocyte CR genes PNPLA6 (j), GPCPD1 (k) and CHDH (l) in the PFC of individuals with cognitive impairment (CI) relative to cognitively resilient (CR) individuals. Representative images (top) show AQP4 transcripts (red puncta) and CR gene transcripts (blue puncta). Scale bars, 20 μm (j–l). Quantification (bottom) was performed using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests; P = 0.0249 (j), P = 0.0052 (k), P = 0.0375 (l). Data are mean ± s.e.m. PNPLA6: n = 3 (CI) and n = 4 (CR) individuals; GPCPD1 and CHDH: n = 4 individuals per group. m, Schematic of choline metabolism and polyamine biosynthesis; significant astrocyte CR genes are highlighted.