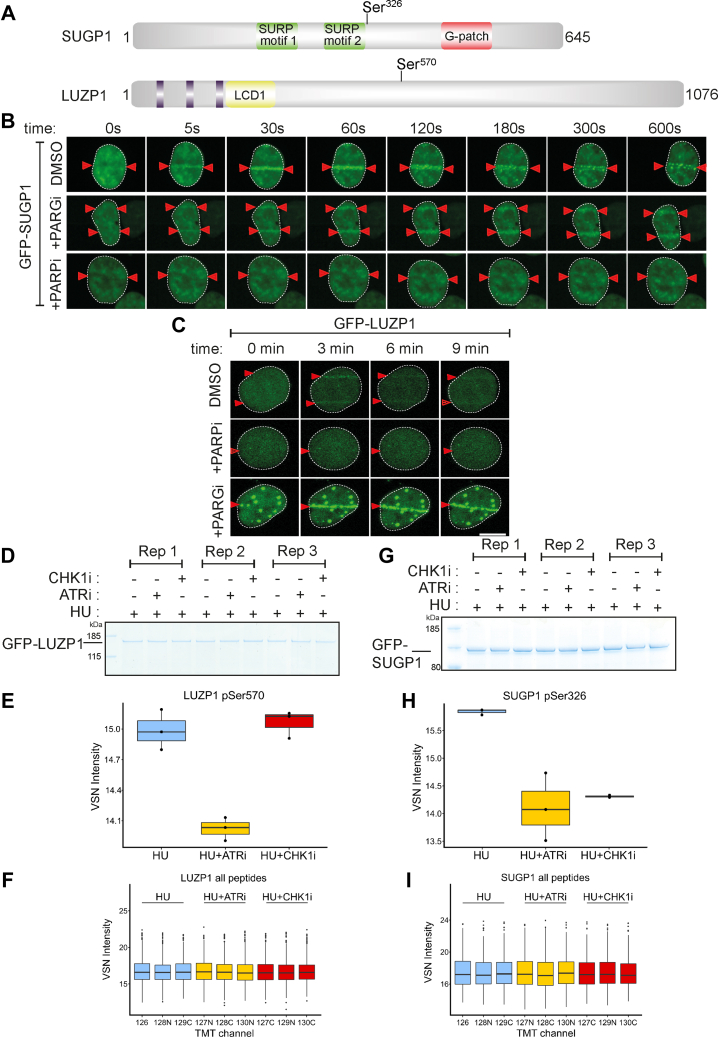
Fig. 4.
Phosphorylation of SUGP1 and LUZP1 and recruitment to DNA damage sites. A, schematic diagram showing the domain organization of SUGP1 and LUZP1. B and C, U-2 OS cells stably expressing GFP–SUGP1 (B) or GFP–LUZP1 (C) were preincubated with DMSO (mock), olaparib (5 μM; PARPi) or PDD00017273 (0.3 μM; PARGi) for 1 h prior to line micro–irradiation. Cells were live-imaged at the times indicated. D, U-2 OS cells were co-transfected with GFP-LUZP1. After 24 h cells were lysed, and cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP-agarose beads. Precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue, and the bands corresponding to the GFP-tagged proteins were excised and processed for mass spectrometric detection of relevant phospho-peptides. Three independent co-transfection experiments were done for every condition (Rep = biological replicate). E, boxplots showing VSN–normalized intensity of phospho-peptides corresponding to LUZP1 pSer570 from the experiments in (D). F, boxplots of the VSN-adjusted TMT reporter ion intensities for all peptides for each TMT label in the case of GFP–LUZP1 from the experiment in (D). G–I, same as D–F except cells were transfected with GFP-SUGP1, and phosphorylation of Ser326 was analyzed in a similar manner. Mass spectrometry raw data was uploaded to ProteomeXchange via jPOSTrepo and can be accessed under the identifier PXD040476. Accompanying data analysis scripts and annotated spectra (66) are available from Zenodo under https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10581706.