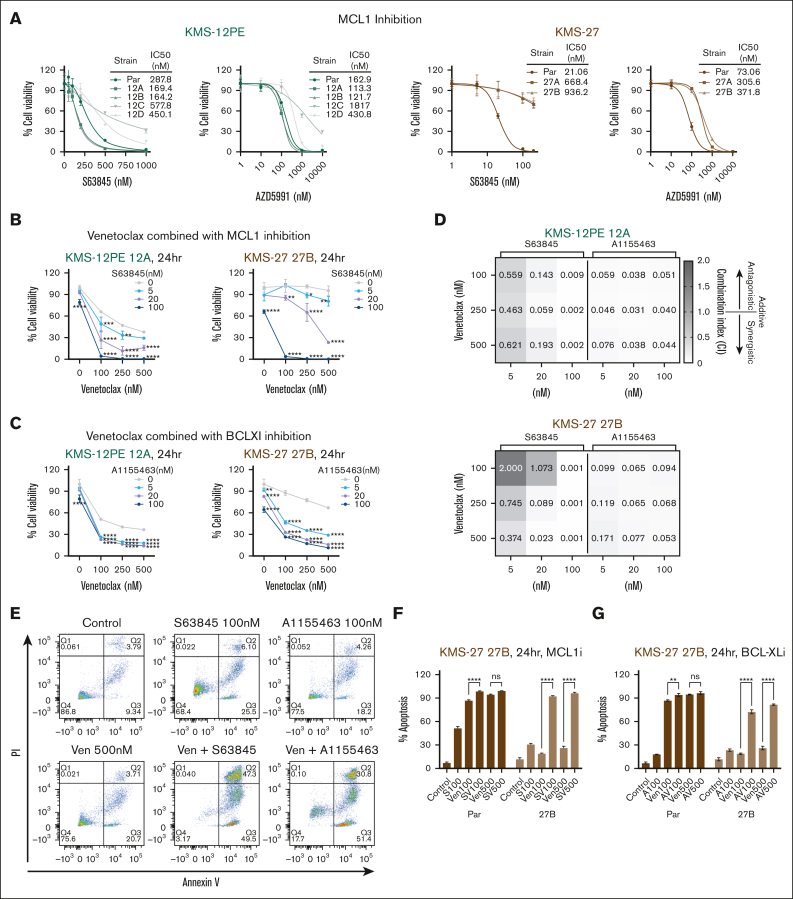
Figure 3.
Dual targeting of BCL2 antiapoptotic members synergistically inhibits cell proliferation of venetoclax-resistant cells. (A) Parental cells and venetoclax-resistant clones were treated with increasing doses of MCL-1 inhibitors (S63845 and AZD5991) for 48 hours. Cell viability was evaluated using CTG and it is expressed as a percentage of cell viability from untreated cells. IC50 values are also shown. (B-C) Venetoclax-resistant clones (KMS12PE clone 12A and KMS27 clone 27B) were treated for 24 hours with a combination of venetoclax and MCL1 inhibitor, S63845 (B), or BCL-XL inhibitor, A-1155463 (C). Cell viability was assessed by CTG assay and represented as percentage of cell viability compared with each untreated control. Two-way ANOVA test was used to calculate statistical significance compared to venetoclax single agent. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 3. (D) Synergism analysis was performed with the CalcuSyn software. Combination index (CI) is represented in the heat map. CI = 1 additive, CI < 1 synergistic, and CI > 1 antagonistic. (E-G) Venetoclax-resistant clone (KMS27 model) were treated with a combination of different BH3 mimetic drugs for 24 hours and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry after annexin V and propidium iodide staining. One representative experiment in resistant clones is shown in panel E. The bar graph in panels F-G represents the mean percentage of apoptosis (annexin V-positive cells) from 2 independent experiments. SV100: S63845 100 nM + venetoclax 100 nM, SV500: S63845 100 nM + venetoclax 500 nM, AV100: A-1155463 100 nM + venetoclax 100 nM, AV500: A-1155463 100 nM + venetoclax 500 nM. Two-way ANOVA test was used to calculate statistical significance between combination treatment with venetoclax single agent.