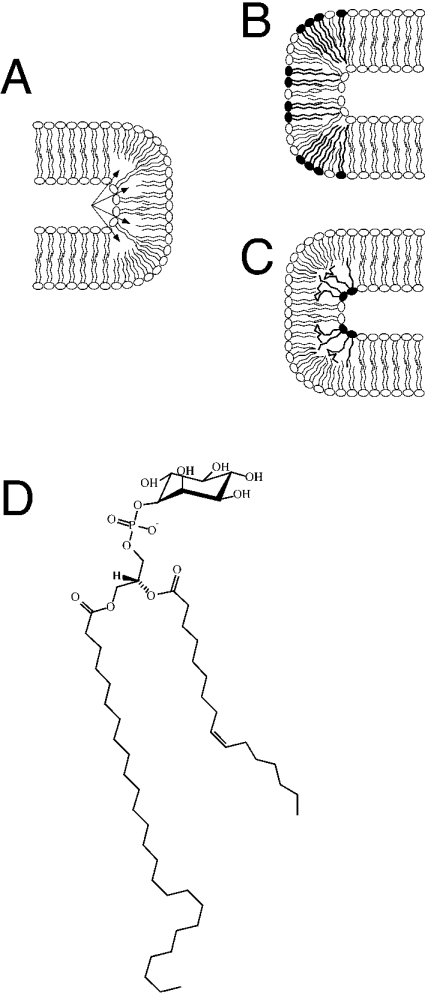
Figure 5. Model of highly curved membrane domains and their possible stabilization by VLCFA-containing lipids: structure of the highly asymmetric C26-PI.
A schematic drawing of a 180° membrane bend with lipids containing LCFAs is shown in (A). A possible formation of a ‘void volume’ within the hydrophobic core of the membrane is indicated by arrows. VLCFA lipids (filled-in head groups) in either the outer (B) or the luminal (C) layer of the membrane could occupy this volume, and thereby stabilize the curved domain. (D) shows the structure of the highly asymmetric C26-PI that was identified in the present study.