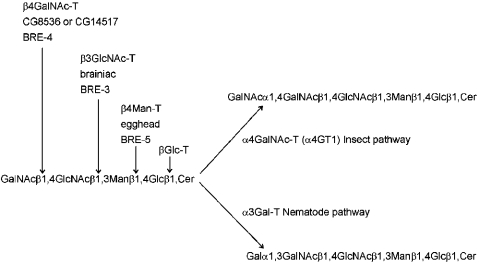
Figure 6. Summary of initial steps of arthro-series glycosphingolipid biosynthesis.
On the basis of structural and genetic information, the first four steps are common to both insects and nematodes. The names of the corresponding enzymes are shown (generic name followed by, for steps 2, 3 and 4, the Drosophila and the Caenorhabditis protein names). The reaction was catalysed by either α4GT1 in Drosophila and a putative α1,3-galactosyltransferase (α3Gal-T) in Caenorhabditis distinguishes the pathways in insects and nematodes. The subsequent steps (not shown) are also not shared by the two phyla. In this scheme, BRE-2, a potential β1,3-galactosyltransferase, would be hypothesized to act after the putative α1,3-galactosyltransferase in the nematode pathway.