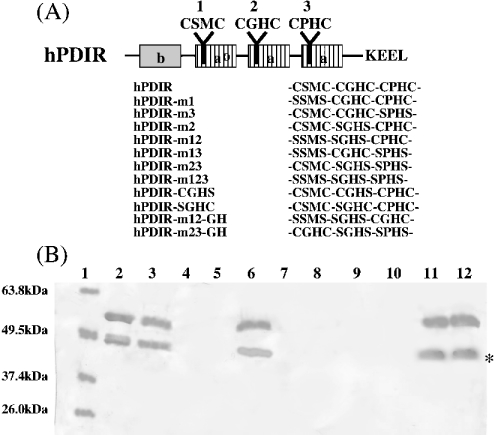
Figure 7. The domain structure of hPDIR, the sequences of its mutants and recognition of the mutants by the 5E phage antibody by Western blotting.
(A) Domains a, a0 and a′ (striped boxes), redox-active Trx domains; domain b (grey box), redoxinactive Trx domain; and domain c (white box), a putative calcium-binding domain. The C-terminal KEEL sequence is a possible ER-retention signal. (B) Detection of the mutants by the 5E phage antibody by Western blotting. Lane 1, marker proteins; lane 2, hPDIR-m1; lane 3, hPDIR-m3; lane 4, hPDIR-m2; lane 5, hPDIR-m12; lane 6, hPDIR-m13; lane 7, hPDIR-m23; lane 8, hPDIR-m123; lane 9, hPDIR-CGHS; lane 10, hPDIR-SGHC; lane 11, hPDIR-m12-GH; lane 12, hPDIR-m23-GH. hPDIR is shown in Figure 2. The 5E phage antibody (1011 pfu/ml) was used with each protein (approx. 5 μg).