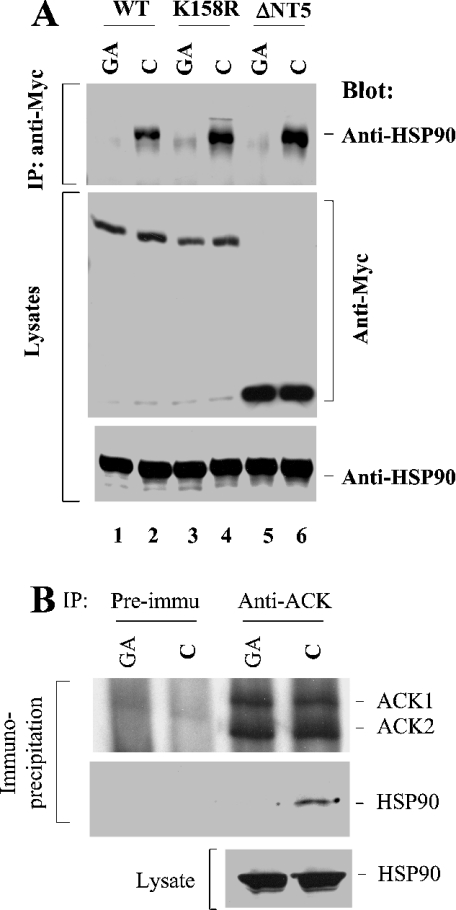
Figure 3. The ATPase activity of HSP90 is essential for its interaction with ACK2.
(A) COS7 cells were transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type ACK2, the kinase-dead mutant ACK2(K158R) or the N-terminal truncation mutant ΔNT5 for 48 h. Before harvesting the cells, 10 μM of the HSP90-specific ATPase inhibitor geldanamycin (GA) or an equivalent amount of DMSO (solvent for geldanamycin; C) was added into the culture medium for 30 min. The cells were immediately lysed and the expressed ACK2 constructs were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-Myc antibody. The co-immunoprecipitated HSP90 was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-HSP90 antibody (top panel). The immunoprecipitated ACK or its mutant was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-Myc antibody (middle panel). (B) Neura-2a cells were serum-starved overnight, then treated with DMSO (control; C) or 10 μM geldanamycin (GA) for 30 min and lysed with lysis buffer. The lysates (1 mg/sample) were subject to immunoprecipitation with anti-ACK-PCC or pre-immune serum. HSP90 in the lysates (bottom panel) and that co-immunoprecipitated with ACK (middle panel) was detected by immunoblotting with anti-HSP90 antibody. The immunoprecipitated ACK was detected by immunoblotting with anti-ACK-PCC (top panel).