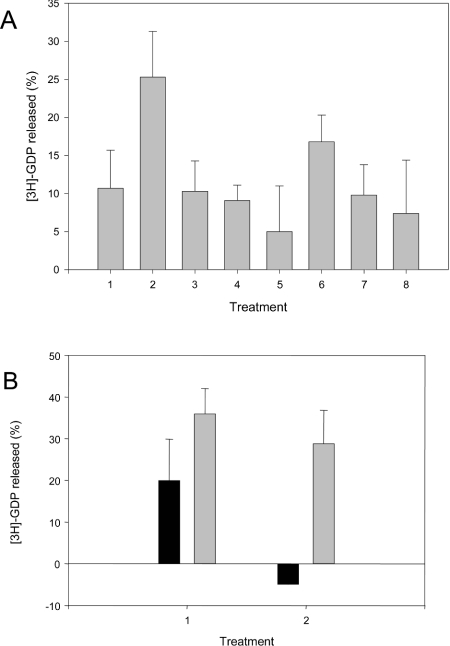
Figure 5. PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-dependent Tiam1 stimulation in vitro is inhibited by inclusion of PtdIns(4,5)P2.
Nucleotide-exchange reactions were carried out as described in the Experimental section, using [3H]GDP-loaded GST–Rac1 as a substrate, for 25 min. Tiam1 GDP/GTP-exchange assays were carried out in the presence of PC/PS vesicles (final concentrations of 233 μM and 90 μM respectively), containing various concentrations of phosphoinositide(s). (A) Assays were carried out with no phosphoinositide (treatment 1), 10 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (treatment 2), 10 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 3), 100 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 4), 1000 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 5), 10 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3+10 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 6), 10 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3+100 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 7), or 10 μM PtdIns(3,4,5)P3+1000 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 (treatment 8). Experiments were also performed using vesicles containing 10 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2 and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3. (B) The GDP/GTP-exchange activity of CamKII-phosphorylated, and non-phosphorylated Tiam1, was determined in the absence (treatment 1), or presence (treatment 2), of 1000 μM PtdIns(4,5)P2. GDP released (%) is the percentage of [3H]GDP that is released from [3H]GDP-Rac1 during the assay. Results are means±S.E.M. for four independent experiments.