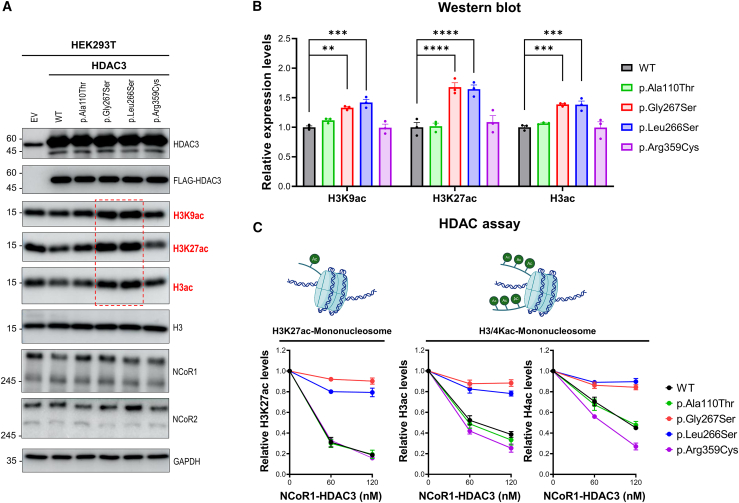
Figure 2.
HDAC3 variants near catalytic sites display deficient HDAC activity
(A) Western blot analyses were conducted on HEK293T cells transduced with either empty vector (EV), FLAG-tagged wild-type (WT) HDAC3, or selected HDAC3 variants (p.Ala110Thr, p.Gly267Ser, p.Leu266Ser, and p.Arg359Cys) using a lentiviral expression system. The detection of HDAC3; FLAG-HDAC3; acetylated histones H3K9, H3K27, and H3; total H3; NCoR1; NCoR2; and GAPDH (loading control) was visualized. Notably, increased acetylation levels of H3K9, H3K27, and H3 were observed in p.Gly267Ser and p.Leu266Ser variants (red dashed rectangle), indicating a defective deacetylation function.
(B) Quantitative analysis of acetylation levels at histone sites H3K9, H3K27, and H3 from (A). The p.Gly267Ser and p.Leu266Ser variants show increased acetylation levels compared to the WT at H3K9, H3K27, and H3, indicating impaired histone deacetylation function. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, n = 3/data point. Data are plotted as mean ± SD.
(C) HDAC assays were performed using H3K27ac-mononucleosomes or H3/H4Kac-mononucleosomes as substrates at various concentrations (0, 60, 120 nM) in conjunction with 100 nM of acetylated mononucleosomes. The deacetylation activities of complexes comprising either the NCoR1 DAD domain-HDAC3 WT or variant forms were measured for histone H3K27ac, H3ac, and H4ac in triplicate (n = 3/data point). The results are plotted as mean ± SD. The p.Gly267Ser and p.Leu266Ser variants do not result in histone acetylation levels, indicating defective HDAC activity. In contrast, the p.Ala110Thr and p.Arg359Cys variants retain deacetylation activities comparable to the WT form.