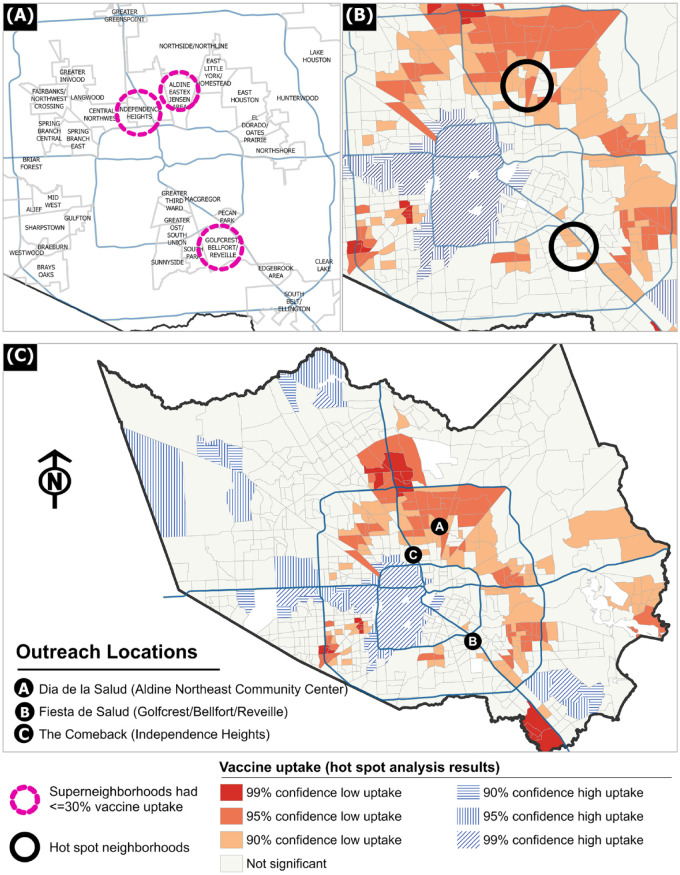
Figure 1.
Superneighborhoods identified for outreach based on low COVID-19 vaccine uptake, Houston, Texas, 2022. Three iterative steps were used to identify focus neighborhoods for community outreach. (A) Identify the tracts where ≤30% of the population was fully vaccinated as of August 10, 2021, and then identify the superneighborhoods that intersected the low-vaccine-uptake tracts. (A superneighborhood groups contiguous communities that share common characteristics. 29 ) (B) Perform hot-spot analysis to identify significant spatial clusters of tracts with low vaccine uptake (ie, hot spots). Several tracts on the eastern and north-central part of the county were hot spots. (C) Reach out to known/connected community stakeholders that worked in and around neighborhoods that were identified during the first step (≤30% uptake) or the second step (hot spots). Three neighborhoods were chosen for outreach based on the ability of community partner organizations to facilitate engagement with key stakeholders. Vaccination data were from the Harris County Health Department. Spatial data processing was performed in ArcGIS Pro 2.8 (Esri).