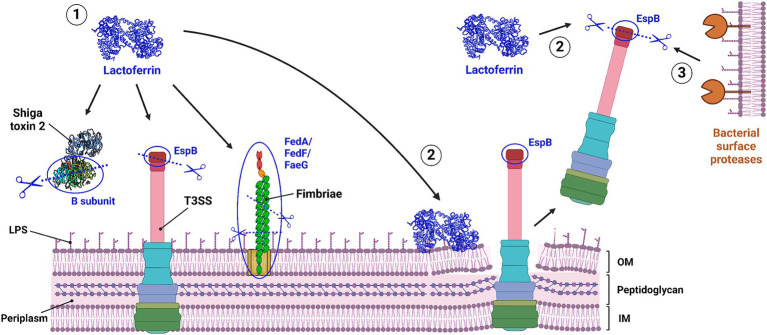
Figure 3.
Three proposed mechanisms for the proteolytic degradation of bacterial virulence factors by lactoferrin. (1) Direct degradation, where lactoferrin directly breaks down bacterial virulence factors. (2) Indirect degradation, where lactoferrin binds to LPS structures on the outer membrane, causing membrane disruption, leading to the release of bacterial virulence factors, which LF then degrades. (3) Induced degradation, where membrane disruption by LF binding triggers the degradation of released virulence factors by bacterial surface proteases. IM, inner membrane; LF, lactoferrin; LPS, lipopolyssacharide; OM, outer membrane; T3SS, type 3 secretion system. Created with Biorender.com.