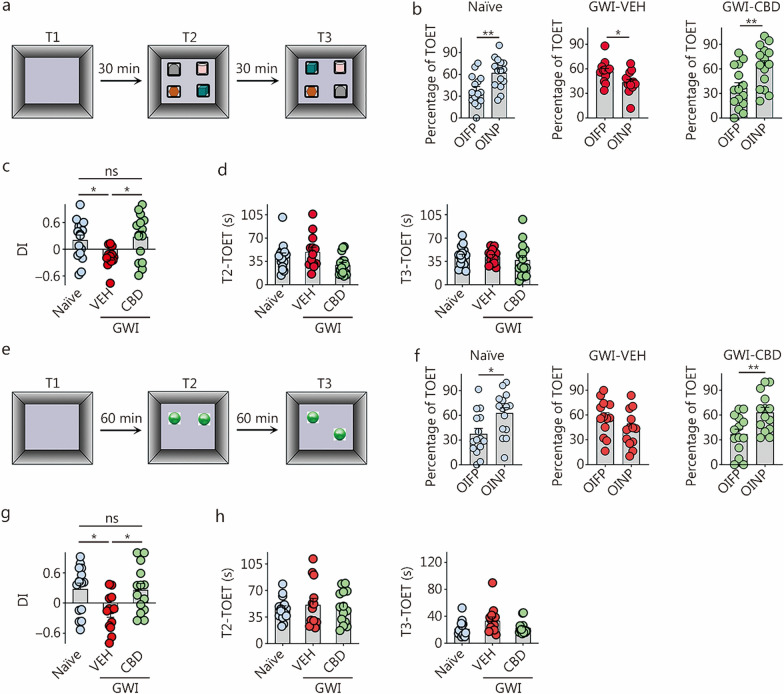
Fig. 2.
CBD treatment enhanced associative recognition and object location memory in rats with chronic GWI. a The cartoon illustrates the sequence of trials in an OIPT. b The bar charts compare percentages of the TOETs spent with the OIFP and the OINP in different animal groups (naïve, n = 15; GWI-VEH, n = 13; GWI-CBD, n = 15). c The bar chart compares the OINP-DI values across groups. d The bar charts compare the TOETs across groups in T2 and T3. e The cartoon illustrates the sequence of trials in an OLT. f The bar charts compare percentages of the TOETs spent with the OIFP and OINP in different animal groups (naïve, n = 15; GWI-VEH, n = 13; GWI-CBD, n = 14). g The bar chart compares the OINP-DI values across groups. h The bar charts compare the TOETs across groups in T2 and T3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns non-significant. Please refer to Tables S3 and S4 in Additional file 1 for detailed statistical information. CBD cannabidiol, GWI Gulf War Illness, OIPT object-in-place test, OIFP objects in familiar place, OINP objects in novel place, VEH vehicle, DI discrimination index, TOET total object exploration time, T trial, OLT object location test