Fig. 5.
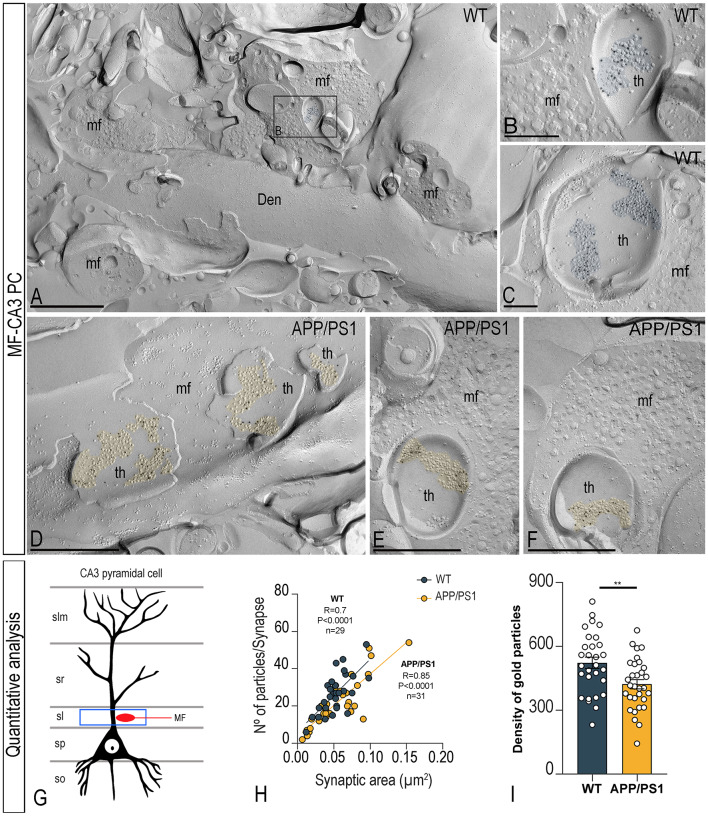
Reduced density of synaptic NMDARs in CA3 pyramidal cell-mossy fibre synapses of APP/PS1 mice. Electron micrographs of thorny excrescence (th) of pyramidal cells making excitatory synapses with mossy fibre terminals (mf) in the stratum lucidum of the CA3 field immunolabelled for GluN1, as detected using the SDS-FRL technique in wild type and APP/PS1 mice at 12 months of age. (A-F) Panel A shows a low-magnification image of the P-face of a thick dendrite (Den) of a CA3 pyramidal cell receiving several mf terminals in wild type mice. Electron micrograph in panel B shows a high-magnification image of the boxed area shown in panel A. Immunoparticles for GluN1 were distributed on thorny excrescence (th) of pyramidal cells making excitatory synapses with mf terminals in wild type and APP/PS1 mice. Scale bars: A,D, E,F, 500 nm; B,C, 200 nm. (G) Drawing of a CA3 pyramidal cell, with the blue box delineating the area used for the quantitative analysis in the stratum lucidum (sl). (H) Scatterplots of the number of immunoparticles for GluN1 versus size of excitatory synapses in the stratum lucidum in both wild type and APP/PS1 mice. There is a strong positive linear correlation between immunoparticle number and synaptic size (Pearson’s correlation test). (I) Mean densities of GluN1 in excitatory synapses in thorny excrescences in the hippocampal CA3 field in wild type and APP/PS1 mice. A significant reduction in the density of NMDAR immunoparticles were detected in APP/PS1 mice compared to age matched wild type (n = 3 animals per genotype; unpaired t-test, **P < 0.01)