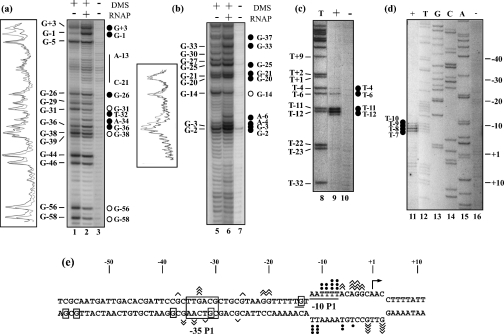
Figure 2. Numerous DNA–protein contacts take place in the gapA P1 RPo.
RPos were formed with the commercial Eσ70 RNAP and the supercoiled pBS::EcogapA plasmid under conditions described in the Experimental section. Probing experiments were performed on the RPo (RNAP+) and on the naked DNA (RNAP–) with DMS (a, b) or KMnO4 (c, d) (see the Experimental section). DMS modifications were followed by piperidine treatment for strand cleavage at modified G and A residues. A control elongation was performed without chemical treatment [lane 3 in (a) and lane 7 in (b)]. Positions of DMS and KMnO4 modifications were identified by primer extension using primer 352 for the template strands (a) and (c) and primer 1043 for the non-template strands (b) and (d). The T sequence ladder in (c) and A, C, G and T sequence ladders in (d) were obtained with primer 1043. Positions of the modified residues in the gapA P1 sequence are given on the left of the panels. The transcription start site was at position +1. Nucleotides that become protected in RPos or nucleotides with an enhanced reactivity compared with DNA are indicated by open and full circles respectively. Densitograms of portions of lanes 1, 2, 5 and 6 were made with the Molecular Analysis software (Bio-Rad). Black lines correspond to lane 1 or 5 (RNAP–) and grey lines to lane 2 or 6 (RNAP+). (e) Compilation of the results of the probing experiments. Angular brackets and closed circles indicate positions of nucleotides whose reactivity to the probe (DMS or KMnO4) is enhanced in the presence of RNAP. Their number is proportional to the level of increase. Boxed nucleotides were less sensitive to the chemical probe in the RPo than in the naked DNA. The −10 sequence and the TG extension are underlined and the −35 sequence is boxed. The opened DNA region is shown as well as the transcription initiation site (broken arrow).