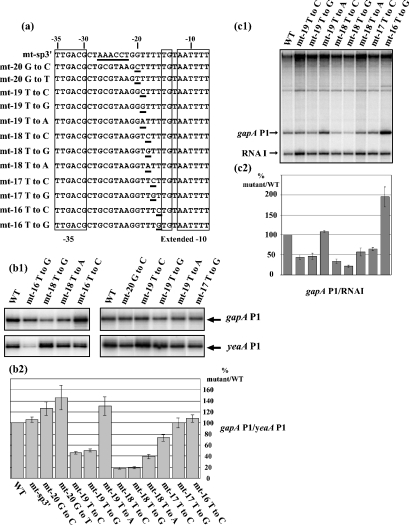
Figure 4. The sequence of the spacer region is important for gapA P1 activity.
(a) The variant gapA P1 promoters with mutations in the spacer region that were produced are represented. The −35 and the extended −10 regions are boxed. The mutated residues are underlined. Names of the mutant promoters are given on the left. (b1, b2) Activities of the variant promoters were measured in vivo as described in Figure 1. Results are expressed as a percentage of the gapA P1/yeaA mRNA level in cells containing the WT gene. The given values are mean values for three independent experiments. The estimated error is indicated by a thin vertical bar. (c1) Plasmid pRLG::gapAP1 carrying the WT promoter and its derivatives, which were carrying gapA P1 promoters mutated in the spacer region, were used as templates for in vitro run-off transcription assays [28]. The transcription products were fractionated on a denaturing gel. (c2) As in Figure 3, the RNA I transcript was used for normalization of the amount of gapA P1 transcript recovered after each transcription experiment. Variations of the gapA P1 activity for the variant promoter are expressed as a percentage of the gapA P1/RNAI ratio found for the WT promoter (100%).