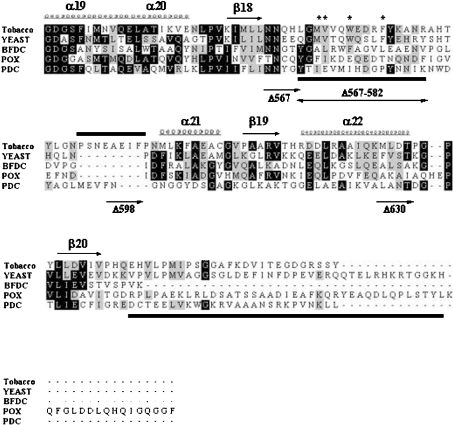
Figure 1. Alignment of the C-terminal region of various ThDP-dependent enzymes.
The sequences of the C-terminal region of various ThDP-dependent enzymes were analysed by amino acid alignment with the ClustalX program. Represented secondary structure, α-helix (α19–α22) and β-pleated sheet (β18–β20), was based on the X-ray crystal analysis of yeast AHAS. The indicated region (residues 549–687, yeast) is a part of the γ-domain of AHAS. The corresponding region of tobacco AHAS shown in this Figure is residues 536–669. BFDC is from Pseudomonas putida; POX is from Lactobacillus plantarum; PDC is from Zymomonas mobilis. Conserved residues are represented with a black shaded box, and residues with similarities are shown with a grey shaded box. An asterisk (*) represents the residues corresponding to herbicide-resistance for AHAS and the bars beneath the sequences indicate the two invisible (disordered) regions in the three-dimensional structure of yeast AHAS, which is postulated to be involved in enzyme catalysis by covering the active site. Also, sequences unique to plant AHASs, tobacco (590–598), Arabidopsis thaliana (591–599) and Brassica napus (576–583, Bna1) are represented by a bar above the sequences. Each C-terminal-truncated mutant has a portion of the C-terminal region of tobacco AHAS as follows: AHAS Δ567, AHAS without entire C-terminus including both mobile loop and the C-terminal lid; AHAS Δ567–582, internal deletion mutant AHAS without the mobile loop; AHAS Δ598, AHAS containing the mobile loop and unique plant sequences, but with the remainder of the C-terminus deleted; AHAS Δ630, AHAS without the regions corresponding to the C-terminal lid of yeast AHAS.