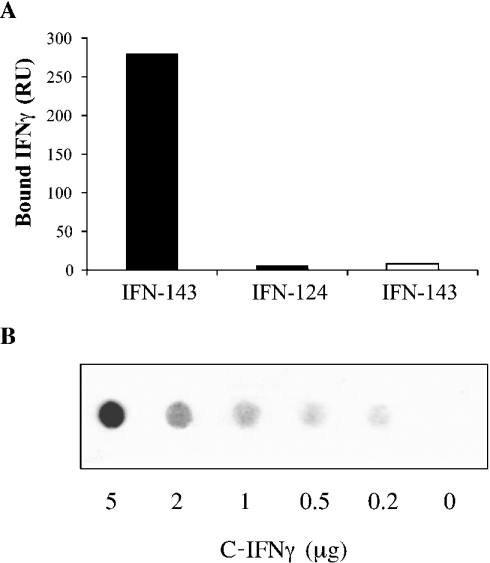
Figure 1. Surface-plasmon-resonance-based binding of IFNγ to immobilized heparin and filter analysis of C-IFNγ–heparin interaction.
(A) IFNγ (IFN-143) or C-terminal-domain-deleted IFNγ (IFN-124), both at 0.5 μg/ml, were injected over a Biacore F1 sensorchip containing streptavidin alone (open bar) or streptavidin plus 100 RU of heparin (closed bars) for 5 min. The surface plasmon resonance signals (in RU) were recorded at the end of the injection phase. (B) Biotin-labelled heparin (0.5 μg/ml) was co-incubated with a range of C-IFNγ concentrations, and bound material was recovered by filtration through a nitrocellulose membrane. Retained biotinylated heparin was revealed by chemiluminescent assay.