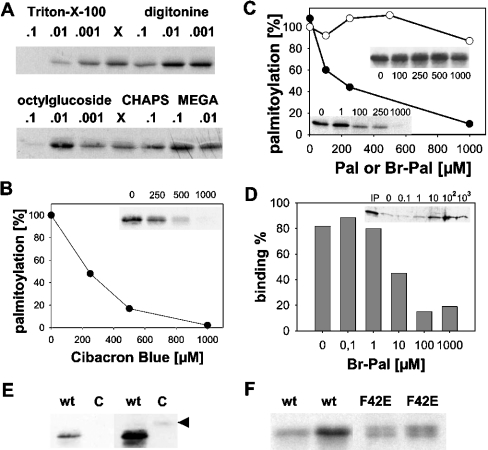
Figure 4. Acylation of hYkt6 requires it N-terminal domain.
(A) Triton X-100, digitonine, octyl glucoside, CHAPS and MEGA-8 were added to the palmitoylation reaction at the indicated concentrations (%, v/v). X, no additions. (B) The palmitoylation reaction was incubated with soluble Cibacron Blue at a final concentration of 0, 250, 500 or 1000 μM. (C) The palmitoylation reaction was incubated with Br-Pal (● and lower left inset) at a final concentration of 0, 1, 100, 250 or 1000 μM. Palmitate (○ and upper right inset) added at a final concentration of 0, 100, 250, 500 or 1000 μM served as control. (D) hYkt6 (4 μg) was incubated with immobilized Cibacron Blue (30 μl) in the presence of 0, 0.1, 1, 10, 100 and 1000 μM Br-Pal. Cibacron Blue with bound hYkt6 was pelleted, the supernatant was precipitated with trichloracetic acid and analysed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. IP, input material. (E) An 8 μg portion of GST–hYkt6–C-terminal domain (C) or full-length hYkt (wt) were incubated with [3H]Pal-CoA prior to SDS/PAGE and fluorography. A short (left) and a long (right) exposure of the same gel is shown. Arrowhead, GST–hYkt6–C-terminal domain. (F) Portions (2 and 4 μg) of wild-type hYkt6 (wt) and 8 and 16 μg of [F42E]hYkt6 (F42E) were incubated with [3H]Pal-CoA. Note that purified [F42E]hYkt6 consists of two bands (see Figure 1a) which are both acylated.