Figure 1. ATRA increases CCR5 expression and R5 HIV-1 replication in macrophages.
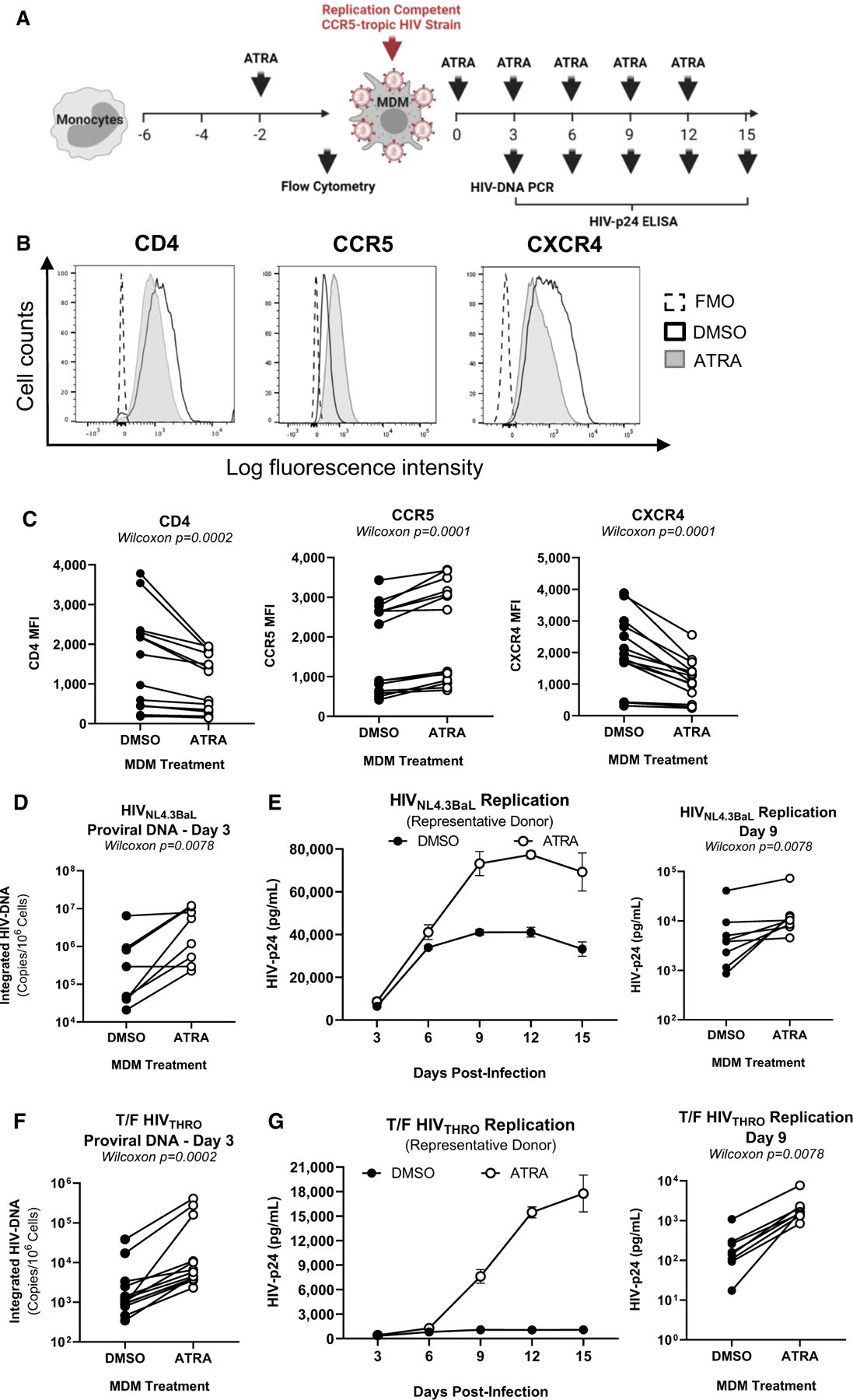
(A) The experimental flowchart. Briefly, monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) were obtained by culturing monocytes in medium containing M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for 6 days. MDMs were exposed (ATRA-MDMs) or not (DMSO-MDMs) to ATRA (10 nM) before and after HIV-1 exposure.
(B and C) Prior to HIV-1 exposure, MDMs were analyzed by flow cytometry upon staining with CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 antibodies. Shown are histograms for CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 expression on MDMs from one representative donor (B), and statistical analysis of CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 MFI expression on MDMs from n = 14 participants. In parallel, MDMs were exposed to replication-competent CCR5-tropic HIV-1 strains (HIVNL4.3BaL; T/F HIVTHRO) and cultured in medium containing M-CSF in the presence/absence of ATRA for 15 additional days. Cell-culture supernatants were collected, and fresh medium containing M-CSF and/or ATRA was added every 3 days.
(D–G) MDMs exposed to HIVNL4.3BaL (D and E) and T/F HIVTHRO (F and G) were analyzed for HIV-DNA integration by PCR at day 3 post infection (D and F) and viral replication by HIV-p24 ELISA every 3 days up to 15 days post infection (E and G). Shown are the kinetics of HIV-1 replication in one representative donor (E and G, left panels) and statistical analysis performed at day 9 post infection for n = 8 participants (E and G, middle and right panels). Wilcoxon p values are on the graphs.
