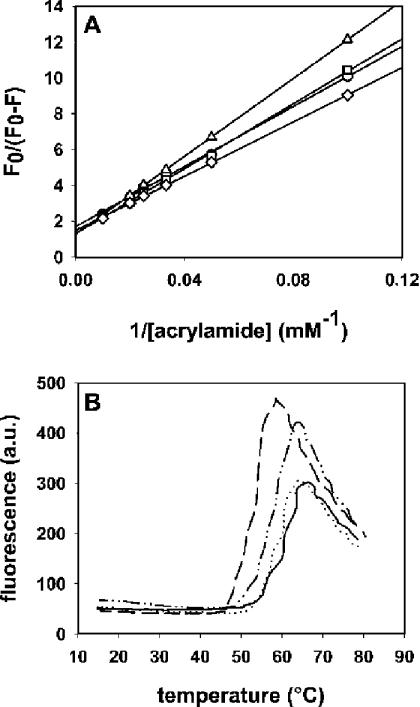
Figure 3. Characterization of the I18W, V22W and A25W mutants.
(A) Stern–Volmer plots for the quenching of wild-type Eqt-II (circles) and mutants I18W (squares), V22W (triangles) and A25W (diamonds) with acrylamide. Excitation wavelength was 295 nm. F0 is the fluorescence intensity in the absence of acrylamide and F is the fluorescence intensity in the presence of different concentrations of acrylamide. The toxin concentration was 350 nM. All measurements were carried out at 25 °C with constant stirring. The buffer used was 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.5/200 mM NaCl. (B) ANS fluorescence as a function of temperature in the presence of Eqt-II (continuous line), I18W (dashed line), V22W (dotted line) and A25W (dashed–dotted line). Toxin concentrations were 6 μM; the ANS concentration was 15 mM. Buffer used was 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.5/200 mM NaCl. The temperature was increased by 1 °C/min. ANS fluorescence was excited at 370 nm, and emission was registered at 468 nm. In both cases, duplicate experiments were performed, producing nearly identical values.