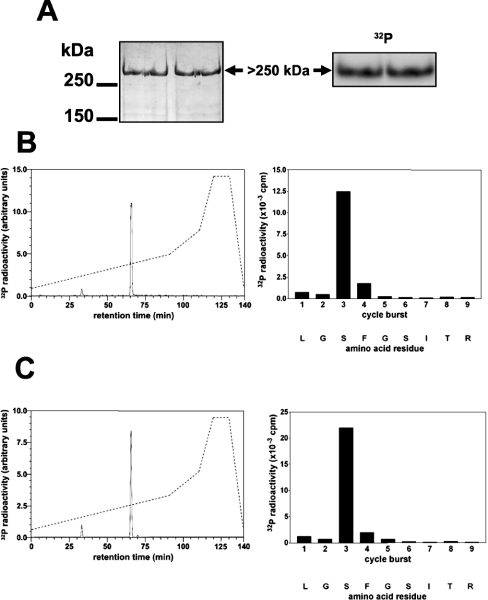
Figure 2. Identification of the residue in FLNc phosphorylated by SGK1 in vitro.
The partially purified PKBα substrate from Figure 1 was phosphorylated by incubation for 30 min with 10 mM MgCl2/0.1 mM [γ-32P]ATP (106 c.p.m./nmol) and 1.0 unit/ml PKBα, denatured in lithium dodecyl sulphate and subjected to SDS/PAGE. (A) The gel was stained with colloidal Coomassie Blue (left panel) or autoradiographed (right panel). (B) The >250 kDa 32P-labelled band from (A) was excised, digested with trypsin and the digest chromatographed on a Vydac C18 column (Separations Group) equilibrated in 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid. The column was developed with an acetonitrile gradient (broken line) at a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min, and fractions of 0.4 ml were collected. The major 32P-labelled peptide P1 (solid line in left panel) was subjected to MS and the sites of phosphorylation were identified by solid-phase sequencing (right panel) after coupling the peptide to a Sequalon-AA membrane [33]. (C) Same as (B), except that GST–FLNc-(1915–2446) was used instead of partially purified human FLNc.