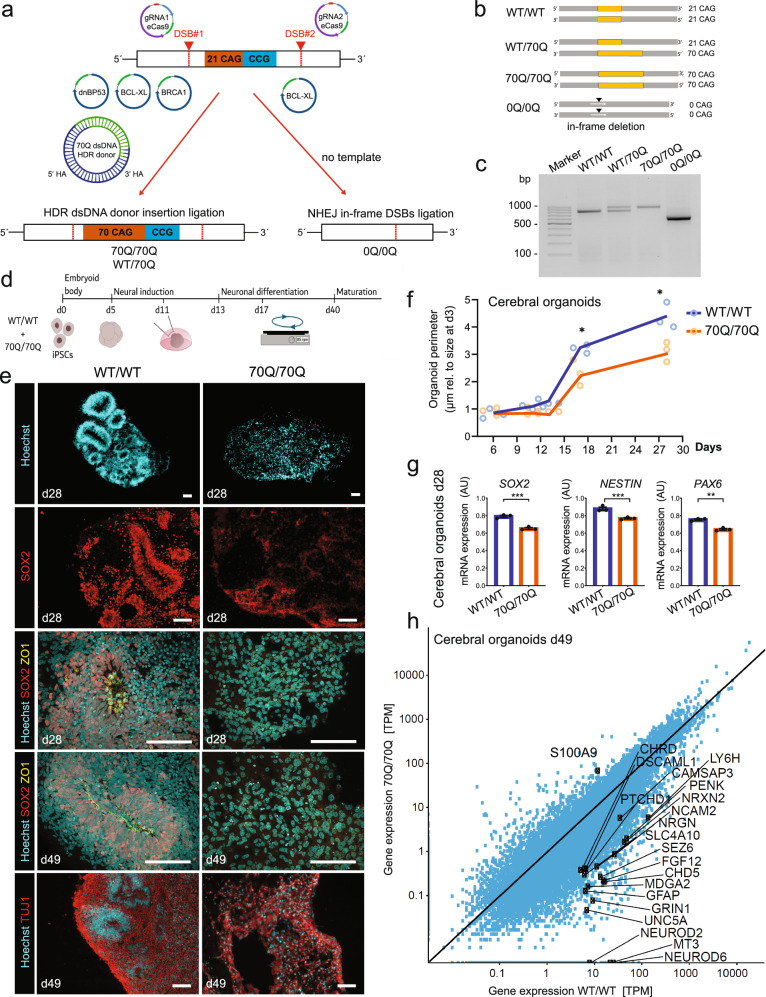
Fig. 1. Engineered iPSCs carrying mHTT give rise to neurodevelopmentally impaired cerebral organoids.
a Genome editing approach in control iPSCs (WT/WT) using two double-strand breaks (DSB) sites to modify the HTT genomic region encompassing the CAG/CAA and CCG repeats stretches. To generate iPSCs carrying elongated CAG in one allele (70Q/WT) or in both alleles (70Q/70Q), we promoted homology direct repair (HDR) (with plasmids BCL-XL and BRCA1), inhibited non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) (with plasmid dnBP53), and provided a HDR donor dsDNA plasmid carrying 70Q repeats and homology arms. We harnessed NHEJ to obtain iPSCs with in-frame deletion of the CAG/CCG region (0Q/0Q). b Overview of the engineered isogenic iPSC lines. c PCR analysis of HTT in the isogenic iPSC lines. Data were repeated in three independent experiments. d Schematics of the protocol to generate unguided cerebral organoids from isogenic iPSC lines WT/WT and 70Q/70Q. e Immunostaining in cerebral organoids at day 28 and 49 showing defective cytoarchitecture and neural progenitor cell (NPC) organization in 70/70Q. Data were repeated in three independent experiments. Scale bar: 100 µm. f Growth rate of cerebral organoids with respect to the initial perimeter size measured at day 3. n = 3 independent organoid differentiations (dots) per line. Each dot represents the average size of all cerebral organoids measured in one biological replicate. *p < 0.05 WT/WT vs. 70Q/70Q; unpaired two-tailed Welch t test. g qPCR analysis of NPC markers in cerebral organoids at day 28. Mean ± s.e.m.; n = 3 independent biological replicates (dots) per line; ***p < 0.001 WT/WT vs. 70Q/70Q; unpaired two-tailed t test (AU=arbitrary units). Four organoids were pooled for each individual RNA isolation. h Gene expression analysis of cerebral organoids at day 49 highlighting the genes belonging to the GO term “nervous system development” (GO:0007399).