Figure 6.
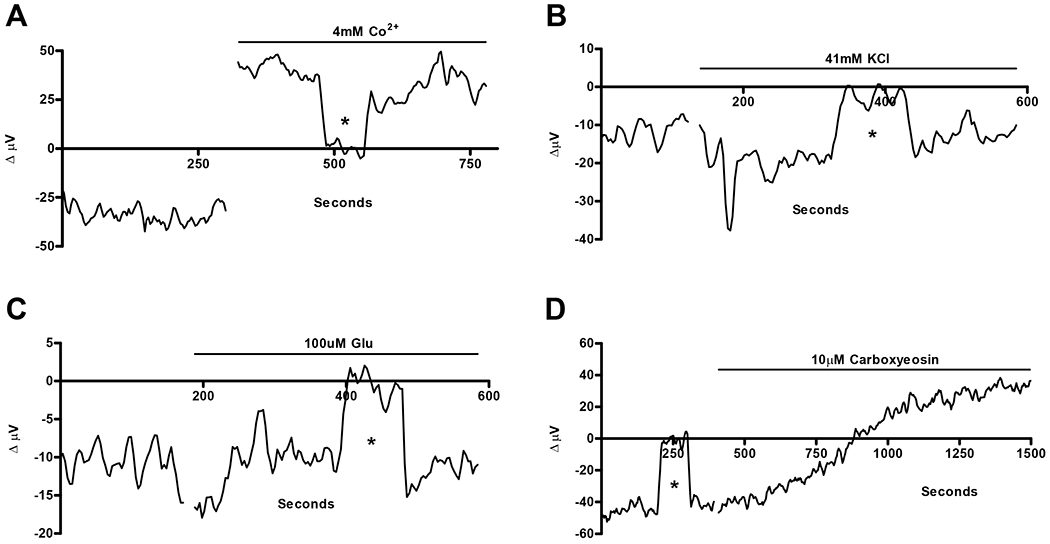
Responses of cells with standing initial negative (alkaline) H+ signals in response to (A) cobalt, (B) high extracellular potassium, (C) glutamate, and (D) carboxyeosin. The calcium channel blocker cobalt reduced the standing alkalinization and turned it into a standing acidic flux, while glutamate and high extracellular potassium were without effect on the standing alkaline flux. Similar to calcium channel blockers, the plasma membrane calcium ATPase blocker, carboxyeosin, also flipped the standing alkalinization to a standing acidic flux.
