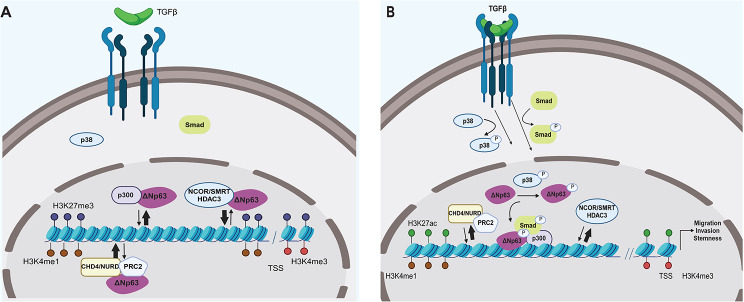
Fig. 7.
Schematic illustration of the effect of active TGFβ signaling on ΔNp63-dependent transcription. (A) In the absence of active TGFβ pathway, ΔNp63 is bound to NURD/PRC2 and NCOR/SMRT/HDAC3 complexes on TGFβ/SMAD target regulatory genomic loci. These regions showing high H3K4me1 are bookmarked for transcription by ΔNp63; however, the presence of the H3K27 tri-methylation mark results in condensed chromatin and inactive transcription. (B) Activation of TGFβ signaling leads to phosphorylation of ΔNp63 at Ser66/68 via p38 MAPK, nuclear translocation of SMAD2/3 transcription factors and complex formation between ΔNp63, SMAD2/3 and p300. p300 catalyzes the acetylation of K27 on H3, which promotes chromatin accessibility and activation of gene transcription favoring cancer cell stemness and invasiveness. Dynamic interactions with chromatin are shown with two anti-parallel arrows. Arrow thickness correlates to the prevalent interaction (association or dissociation). Created with BioRender.com