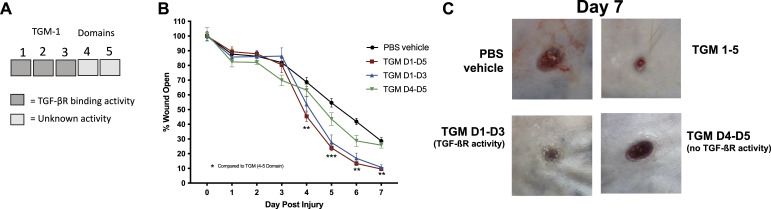
Figure 4. In vivo wound biopsy with truncated variants suggest TGF-β mimic (TGM) enhances wound healing through TGF-ßR activity.
(A) The TGM molecule contains 5 domains. Domains 1 through 3 comprise the TGF-ßR domain activity. The activity of domains 4 and 5 is currently unknown. (B) 5 mm full-thickness excisional wounds were generated on the dorsal skin of C57/Bl6 mice. Wounds were treated with PBS vehicle control or whole TGM (TGM D1-D5; 500 ng) or TGM containing only domains 1 through 3 (TGM D1-D3; 500 ng) or domains 4 and 5 (TGM D4-D5; 500 ng) and covered with Tegaderm for the duration of the study. Wound size analysis was performed on the gross images obtained at each time point during the course of treatment. Treatments were given daily whereas the dressing was changed every other day. Wound closure rate with either a daily dose of topical TGM D1-D5, TGM D1-D3, TGM D4-D5, or PBS vehicle control over 7 d was quantified as the percentage of wound closure at each time point compared with the percentage open at day 0. (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; black stars represent the significance of TGM D1-D5 compared with TGM D4-D5; five independent wounds from each treatment were measured through blinded analysis on ImageJ). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons for comparison between all treatment groups at each timepoint. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. (C) Representative wound images of mice treated topically with PBS vehicle control, TGM D1-D5, TGM D1-D3, or TGM D4-D5 (500 ng) on day 7 provide a visual comparison of the area of wound remaining open between the four different groups. Results from two or more independent determinations demonstrate similar results.