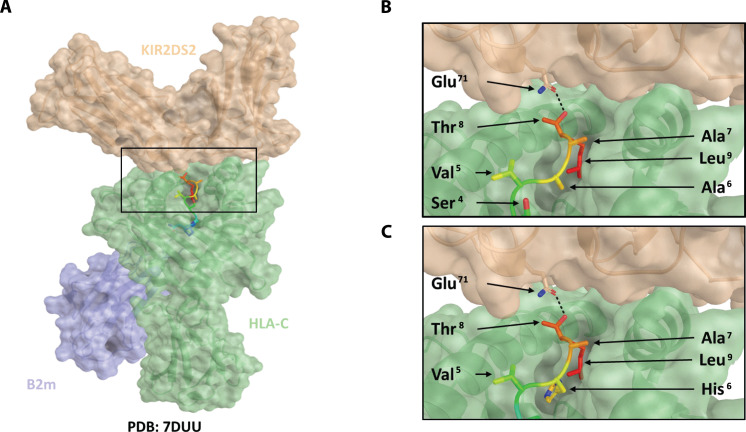
Fig. 2. Modeling of HLA-C*01:02, NAPLVHATL, and KIR2DS2 binding interactions.
On the basis of the crystal structure of the HLA-KIR complex (PDB: 7DUU), a potential binding mode for the XPO1-derived peptide, NAPLVHATL, was investigated using PyMOL. In silico mutagenesis of the peptide was performed using the protein mutagenesis tool within PyMOL, with the minimization of steric clashes being used to determine the optimal rotameric state of the mutated residue. Peptide-protein interactions were analyzed using PISA. KIR2DS2 is shown as a brown transparent surface, HLA as a green transparent surface, and β2-microglobulin as a blue transparent surface. The peptide is shown as a rainbow ribbon backbone with side chains as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as a black dashed line. (A) Model of KIR2DS2 binding with HLA-C*01:02 and NAPLVHATL. Conservation of the KIR2DS2 Glu71–peptide Thr8 hydrogen bond is shown in (B) for the LNPSVAATL crystal structure and in (C) for the modeled NAPLVHATL peptide.