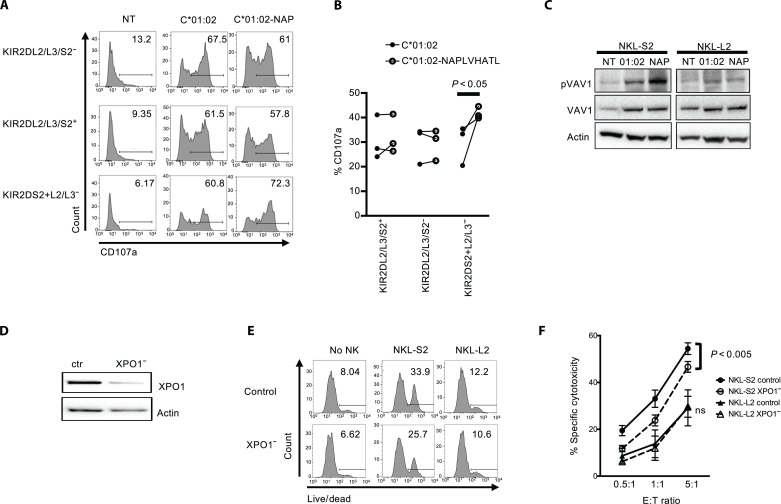
Fig. 3. Endogenously presented NAPLVHATL activates KIR2DS2+ NK cells.
(A and B) 721.221 cells were transfected with HLA-C*01:02 alone (C*01:02) or in combination with the peptide NAPLVHATL (C*01:02-NAP), and the cell lines were used as targets for degranulation assays with interleukin-15–activated NK cells as effectors. CD107a expression on the indicated subpopulations of CD3−CD56+ NK cells was assessed by flow cytometry against these targets. (NT = no target). One representative flow cytometry plots of CD107a expression is shown from six healthy donors tested (A), and degranulation from three patients with HCC is shown in (B). P values were determined by paired t test. (C) NKL-2DS2 or NKL-2DL2 cells were incubated with either no target (NT), 721.221:HLA-C*01:02 (C*01:02) or 721.221:HLA-C*01:02+NAPLVHATL (NAP) cells for 5 min and assessed for Vav1 (Tyr174) phosphorylation by immunoblotting. A representative image from six experiments is shown. (D) Representative immunoblot of XPO1 silencing following XPO1-targeting siRNA treatment of Huh7:HLA-C*01:02 cells. (E and F) Huh7:HLA-C*01:02 cells were treated with control or XPO1-targeting siRNA and used as targets in cytotoxicity assays with NKL-S2 or NKL-L2 cells. Killing was determined using the LIVE/DEAD stain. Representative plots at an E:T ratio of 5:1 are shown in (E), and the mean specific cytotoxicity and SEM from five independent experiments are shown (F). P values were determined by two-way ANOVA.