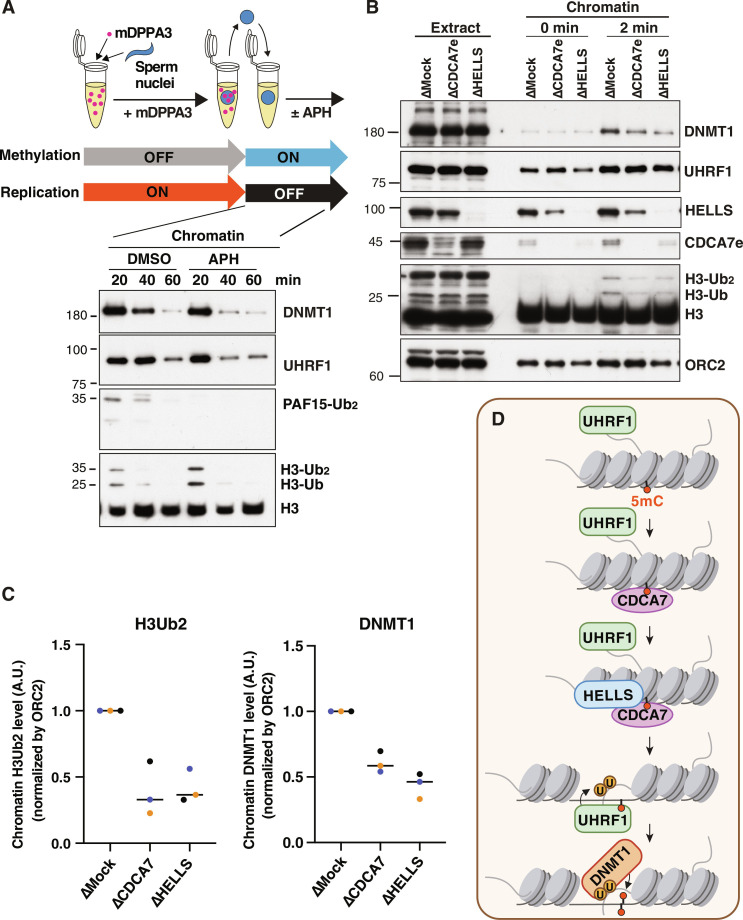
Fig. 7. CDCA7e and HELLS regulate replication-uncoupled maintenance DNA methylation.
(A) Xenopus sperm nuclei were incubated for 120 min in interphase Xenopus egg extract in the presence of 1.1 μM recombinant mDPPA3. Chromatin was isolated and reincubated in interphase egg extract in the presence or absence of 150 mM aphidicolin (APH). (B) Sperm nuclei were incubated for 120 min in mock-depleted extracts, CDCA7e-depleted or HELLS-depleted extracts supplemented with mDPPA3. Chromatin was isolated and reincubated in mock-depleted, CDCA7e-depleted or HELLS-depleted extracts in the presence of aphidicolin. Chromatin was then isolated at 0 and 2 min, and chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using indicated antibodies (left). Representative of n = 3 independent experiments shown. (C) The intensity of dually monoubiquitylated H3 (H3Ub2) and DNMT1 signal relative to chromatin-bound ORC2 signal at 2 min was measured using ImageJ (n = 3). The means of the intensities of three independent experiment are shown as relative value (max = 1.0). Data points from each biological replicate are annotated in a unique color. (D) Schematic of the proposed function of CDCA7/HELLS in DNA methylation maintenance. A hemimethylated CpG in a nucleosome dense region is undetected by the SRA domain of UHRF1. CDCA7 detects the hemimethylated CpG on the nucleosome via the HMZF domain. CDCA7 recruits and activates HELLS, which unwraps DNA from the nucleosome to make the hemimethylated CpG accessible to the SRA domain of UHRF1, promoting its E3 ligase activity to ubiquitylate H3. DNMT1 activated by ubiquitylated H3 executes maintenance DNA methylation. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.