Figure 6.
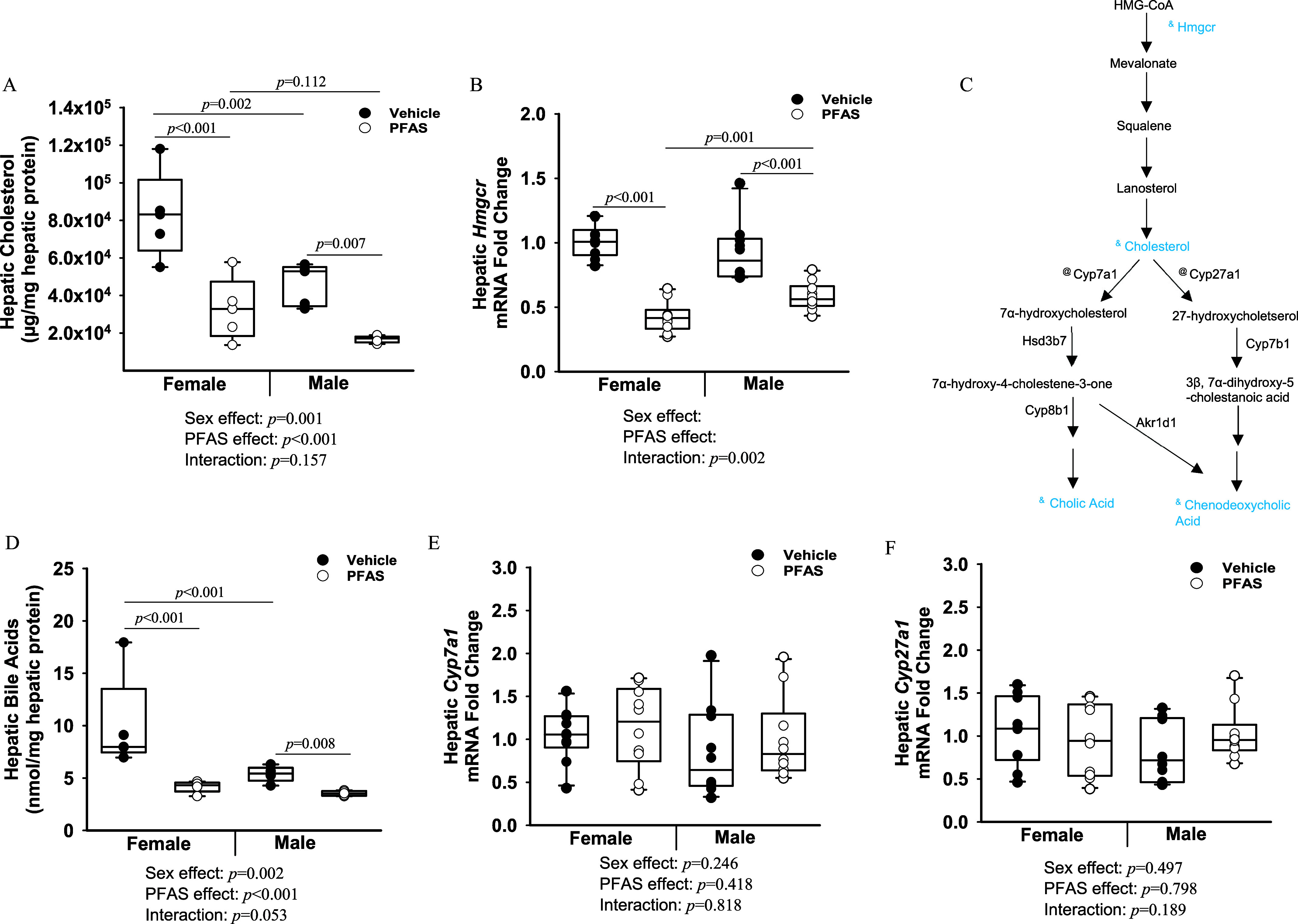
Exposure to the PFAS mixture, hepatic cholesterol and bile acid levels, and synthesis pathways. (A) Hepatic protein was isolated from mice from each treatment group and hepatic total cholesterol levels were measured. (B) Total hepatic RNA ( mice from each treatment group) was isolated, and gene expression levels of Hmgcr were determined by RT-qPCR. (C) Diagram of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis pathways. Steps preceded by “&” represent a significant reduction, whereas those measured and not significantly affected are preceded by “@.” (D) Hepatic total bile acid levels. Gene expression levels of (E) Cyp7a1, and (F) Cyp27a1 were determined by RT-PCR. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. Two-way ANOVA was used to analyze both main effects (i.e., sex, PFAS), as well as the interaction between sex and PFAS (interaction ). The Holm–Sidak post hoc test was used for multiple comparisons. With past consultation from biostatisticians, a significant interaction term supersedes the main effects and can make their meaning unclear. We therefore have not included the main effects -values for any figure with a significant interaction. Box plots represent the median values with upper and lower quartiles; whiskers extend to the 1st and 99th percentiles. Data are reported in Excel Tables S12 and S13. Note: ANOVA, analysis of variance; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; PFAS, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
