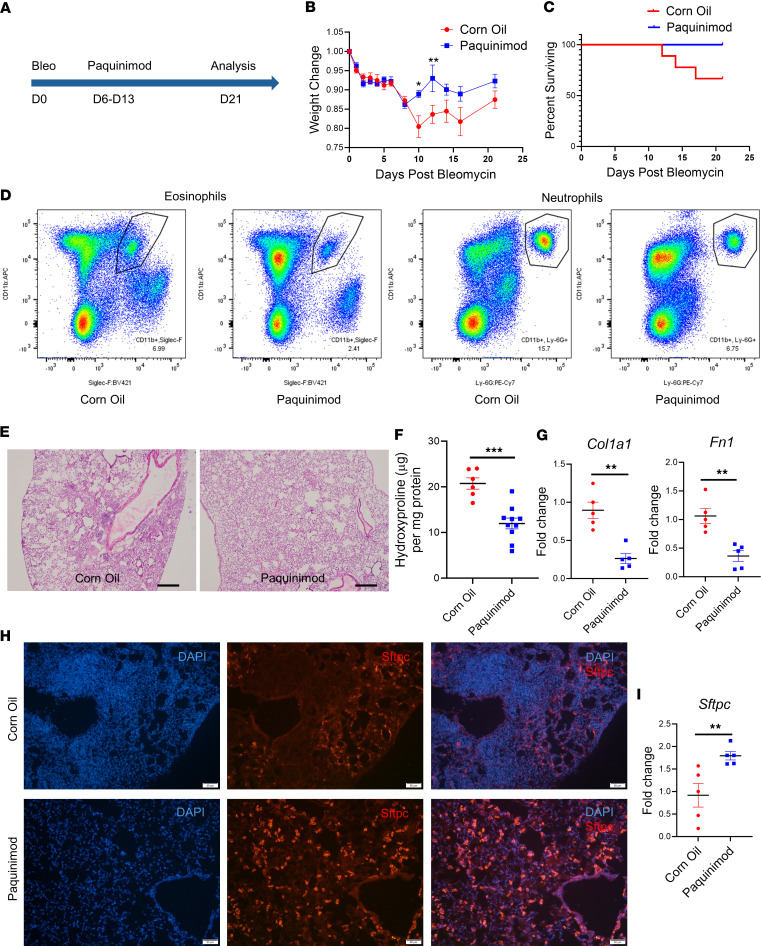
Figure 5. S100A8/9 inhibitor paquinimod alleviates experimental lung fibrosis.
(A) Schematic showing timeline of paquinimod treatment, which inhibits the inflammatory S100A8/9 proteins, in the CebpaΔSftpc mouse model of fibrosis. (B) Weight of mice treated with paquinimod (n = 10) or corn oil (n = 9), as depicted in A. (C) Survival curve for mice from B. (D) Flow cytometry analysis performed 21 days after bleomycin injury, showing eosinophils and neutrophils from the lungs of mice treated with paquinimod (n = 3) or corn oil (n = 3). (E) Representative H&E staining images showing lung sections taken 21 days after bleomycin injury from mice treated with paquinimod (n = 3) or corn oil (n = 3). (F) Hydroxyproline assay performed 21 days after bleomycin injury in lung samples from mice in E. (G) qPCR performed 21 days after bleomycin injury for profibrotic gene transcripts in mice treated with paquinimod (n = 5) or corn oil (n = 5). (H) Representative immunostaining images of Sftpc expression from the lungs of mice harvested 21 days after bleomycin injury and after treatment with paquinimod (n = 3) or corn oil (n = 3). (I) qPCR for Sftpc expression performed 21 days after bleomycin injury in mice from H. Data were analyzed using a Mann–Whitney U test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.