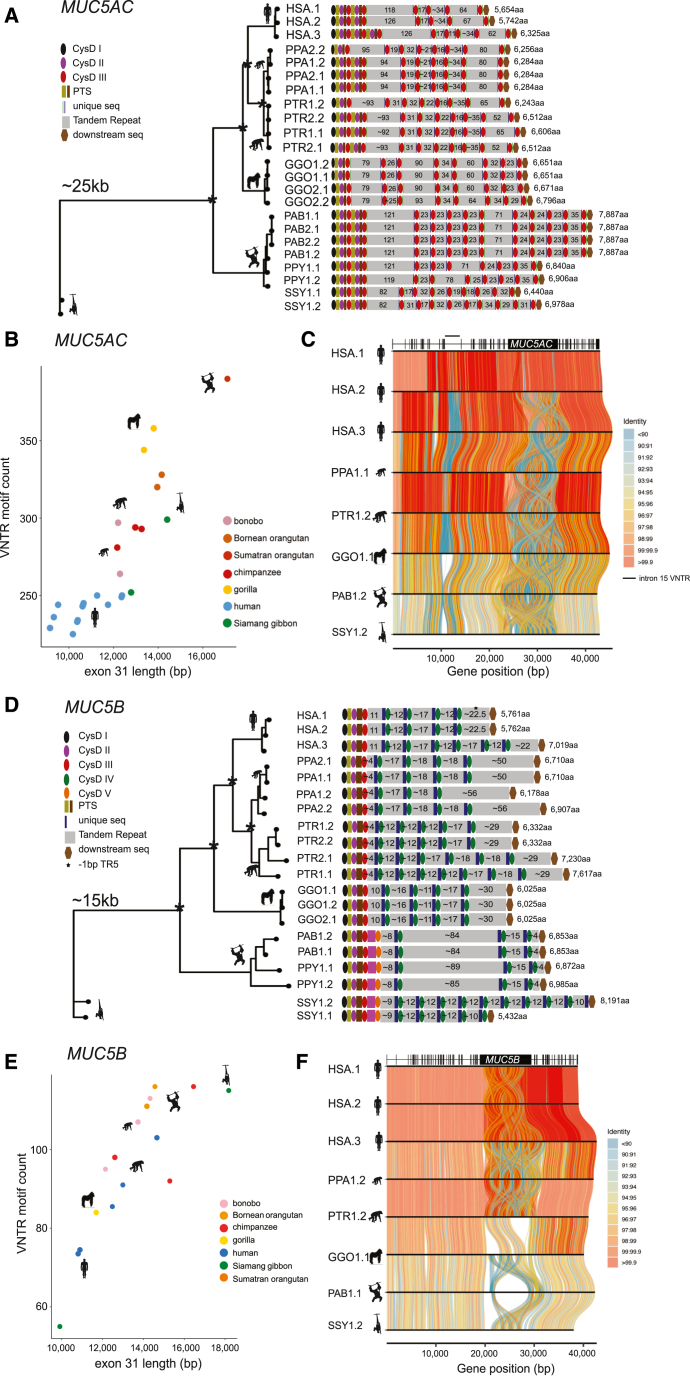
Figure 3.
The genetic architecture of MUC5AC and MUC5B in the nonhuman ape lineages
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of ∼25 kbp from at minimum two haplotypes per ape lineage for MUC5AC and subsequent protein predictions based on human exon boundary alignments. (∗) = central node distinguishing species branches with bootstrap support. Diagrams represent protein domains within the large central exon. HSA denotes human haplotypes.
(B) Scatterplot of total MUC5AC exon 31 length (in base pairs) and total VNTR motif count across all VNTR domains in human and NHPs.
(C) Tiled alignments between representative haplotypes of each ape species (most common or most structurally unique haplotype per species) for MUC5AC. MUC5AC intron/exon boundaries are distinguished by the gene model at the top of the visualization.
(D) Phylogenetic analysis of ∼15 kbp from at minimum two haplotypes per NHP lineage and subsequent protein predictions for MUC5B haplotypes based on human exon boundary liftover. (∗) = central node distinguishing species branches with 100% bootstrap support. Diagrams represent protein domains with the large central exon.
(E) Scatterplot of total MUC5B exon 31 length (in base pairs) and total VNTR motif count across all VNTR domains in human and NHPs.
(F) Tiled alignments between representative haplotypes of each NHP species (most common or most structurally unique haplotype per species) for MUC5B. MUC5B intron/exon boundaries distinguished by gene model at top of visualization.