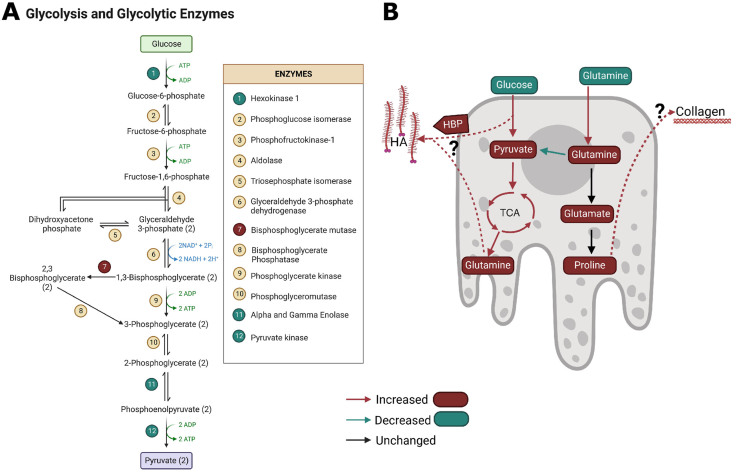
Figure 6.
Dysregulated glycolytic enzymes and a summary of metabolic dysregulation in SFD RPE. A, Schematic showing glycolytic intermediates and the altered glycolytic enzymes identified via proteomics. Enzymes in green circles were found to be decreased while the enzymes in red circles were found to be increased. B) Summary of metabolic dysregulation in SFD RPE. Red arrows and bubbles indicate an increase in abundance/activity while green represents a decrease in abundance/activity. Glucose utilization increases and intracellular pyruvate accumulate while glucose contribution to the TCA cycle and glutamine cataplerosis increases. Glutamine utilization increases and extracellular glutamate accumulates as intracellular glutamate decreases and intracellular glutamine accumulates. Glutamines conversion to pyruvate via malic enzyme is decreased while glutamine anaplerosis, or contribution to the TCA cycle, is unchanged. It remains to be determined which pathway is metabolizing the additional glutamine taken up from the media and generated from glucose. We hypothesize that excess glutamine and glycolytic intermediates could be used to generate hyaluronic acid, through the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway or could be converted to proline and utilized for collagen synthesis. (For interpretation of the references to color/colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)