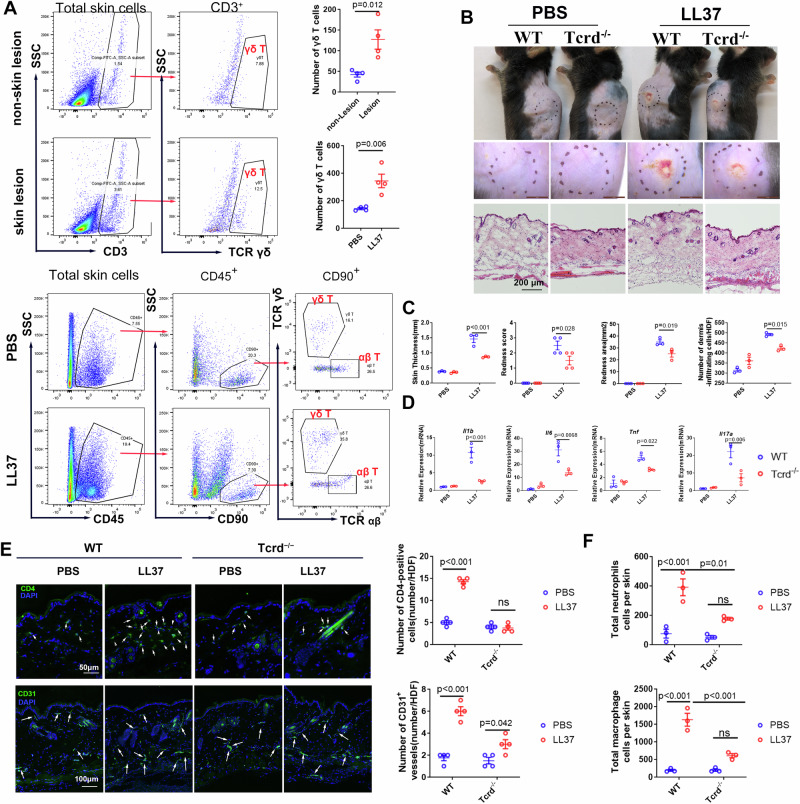
Fig. 6. γδ T-cell infiltration is increased and essential for the pathogenesis of rosacea.
A Representative FACS plots and quantification of γδ T cells in the skin from rosacea patients and rosacea-like mice (n = 4 for each group). B Representative macroscopic images and HE-stained sections and (C) The redness score, area of erythema and skin thickness of skin tissues in WT or Tcrd−/− mice with LL37 or PBS injection (n = 3–4 for each group). D The mRNA levels of rosacea-characteristic factors (n = 3 for each group) and (E) CD4+ T cells infiltration (n = 4 for each group) and CD31+ microvasculature (n = 5 for each group) in the skin of WT or Tcrd−/− mice injected with LL37 or PBS. F The quantification of immune cells in the skin from rosacea-like mice (n = 3 for each group). Data represent the mean ± SEM. ns, p > 0.05. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test was used.