Table 1.
Comparison of PMTCT indicators for pregnant women and newborns who received services at 66 sites in Guinea from 2019 to 2022
| Test PW | HIV-positive PW, n (%) | HIV-positive PW who received ART n (%) |
HIV-positive PW who received ART and delivered at a PMTCT site, n (%) |
Infant exposed to HIV born at a PMTCT site, n (%) |
Infant exposed to HIV who received ARV prophylaxis, n (%) |
Infant exposed to HIV who underwent DNA-PCR testing, n (%) |
Infant exposed to HIV who underwent DNA-PCR testing and had a positive result, n (%) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before intervention (2019–2020) | 465 461 | 8 256 (2%) | 5 467 (66%) | 3 323 (61%) | 3432 (62%) | b5 227 (152%) | 2 205 (42%) | 184 (8%) | |
| After Intervention (2021–2022) | 651 558 | 7 974 (1%) | 7 495 (94%) | 4 840 (65%) | 3988 (53%) | 8 737 (219%) | 3 462 (40%) | 149 (4%) | |
| a% Variation | 40 | -3 | 37 | 45 | 16 | 67 | 57 | -19 | |
| * P value | p = 0.669 | p < 0001 | p < 0001 | p < 0001 | p < 0001 | p < 0001 | p = 0.68 | p = 0.09 | |
* P value Mann‒Whitney Test
a: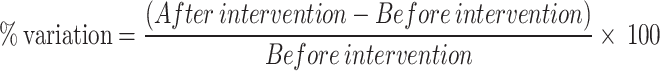
b: the percentage of more than 100% explained by the fact that these sites treated INFANT EXPOSED TO HIV s from other health facilities in the region
