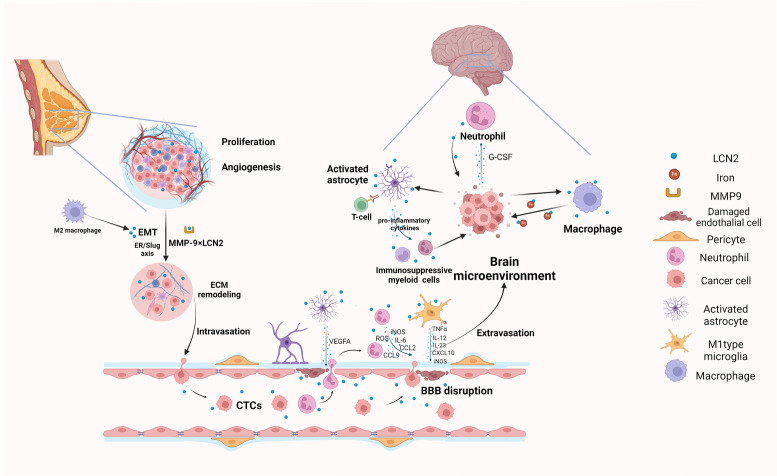
Figure 1.
Graphical summary of biological mechanisms of LCN2 involved in breast cancer brain metastasis (Created with BioRender.com). LCN2 promotes local tumor growth and invasion through angiogenesis, EMT, and ECM remodeling, which are crucial preconditions for cancer cells to intravasate and migrate to the brain. During extravasation, LCN2 disrupts the BBB and facilitates CTCs in penetrating blood vessels into the brain by inducing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from astrocytes, microglia and neutrophils. Finally, the surviving cancer cells colonize and proliferate in the brain by modulating neuroinflammation and creating an immunosuppressive brain microenvironment. EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ECM, extracellular matrix remodeling; CTCs, Circulating tumor cells; BBB, Blood-Brain Barrier.