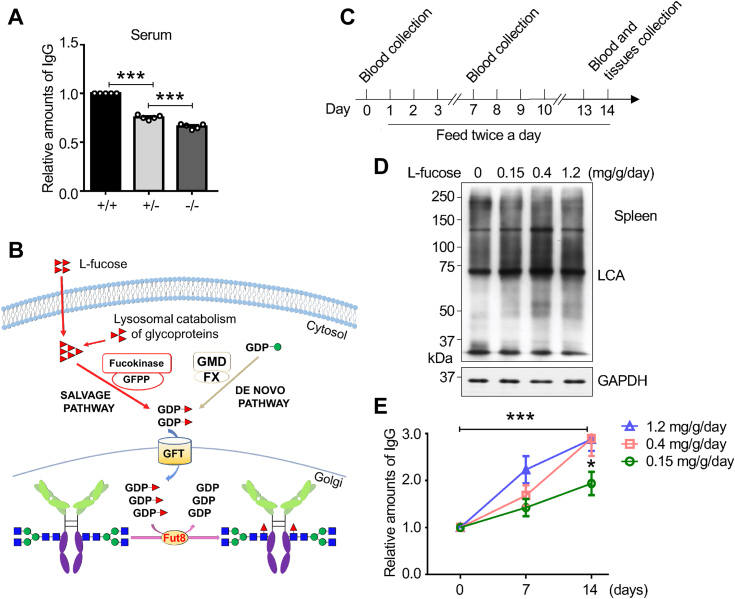
Figure 1.
Effects of exogenous L-fucose on IgG levels and core fucosylation in the spleens of Fut8+/−mice. A, comparison of IgG levels among the Fut8+/+, Fut8+/−, and Fut8−/− mice. IgG was purified by immunoprecipitated in serum as described in “Experimental procedures”. Equal serum (5 μl) was immunoprecipitated by Ab Capcher and detected by anti-mouse IgG antibody. The IgG level of the Fut8+/+ group was set as 1.0 and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis by GraphPad Prism version 6 as the mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. The data were obtained from five mice. B, there are two pathways for producing GDP-fucose in cells: de novo and salvage. The exogenous L-fucose can be metabolized to the GDP-fucose via the salvage pathway and provide more substrate for the biosynthesis of core fucosylation. C, schedule of L-fucose administration with the concentration at 0.15, 0.4, or 1.2 mg/g/day, twice daily, lasting 14 days. Blood was collected on the 0, 7th, and 14th days. D, effects of exogenous L-fucose on core fucosylation in spleen tissues. After the pretreatment described in (C), the same amounts of spleen tissues were extracted and detected using LCA lectin blot. GAPDH was used as a loading control. E, effects of exogenous L-fucose on IgG levels. The data were obtained from at least three mice and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis as the mean ± SEM. The relative levels of IgGs at 0 days were set as 1.0. ∗p < 0.05 ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Fut8+/−, Fut8 heterozygous knockout; Fut8−/−, Fut8 knockout; IgG, immunoglobulin G; LCA, Lens culinaris agglutinin.