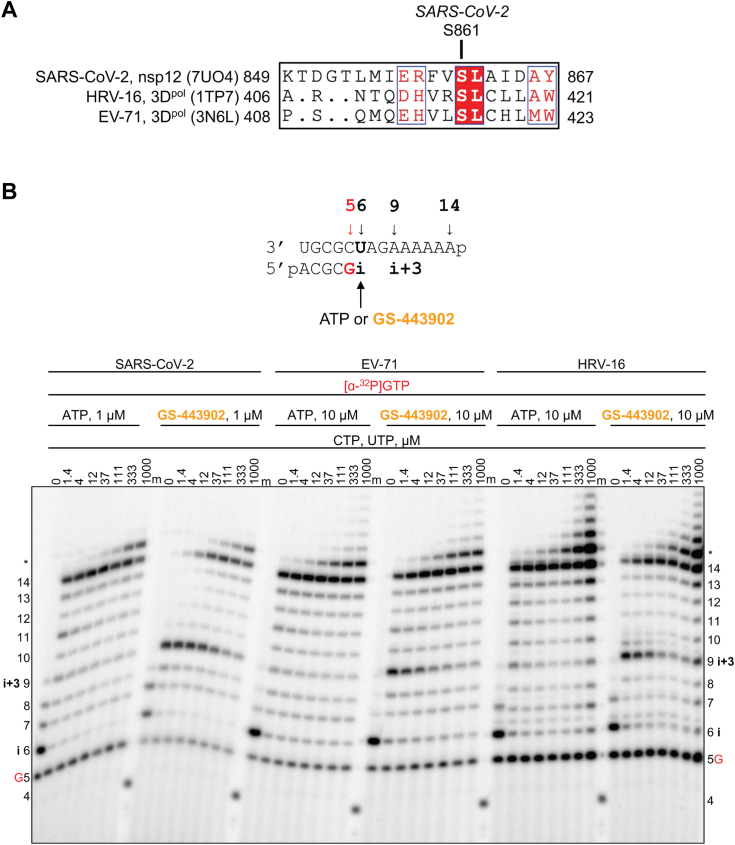
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2, EV-71, and HRV-16 RdRp-catalyzed RNA synthesis pattern of inhibition following a single incorporation of ATP or GS-443902 as a function of nucleotide concentration. A, sequence alignment based on a 3D structural overlay of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12 (PDB:7UO4), HRV-16 3Dpol (PDB:1TP7), and EV-71 3Dpol (PDB:3N6L) composed using ESPript 3.0 (82). Ser-861 (SARS-CoV-2 numbering) is conserved in HRV-16 and EV-71 RdRp. B, RNA primer/template supporting a single incorporation of ATP or GS-443902 at position 6 (top). G indicates incorporation of [α-32P]-GTP at position 5. Extension following the incorporation of ATP and GS-443902 at position 6 (“i”) at increasing CTP and UTP concentrations catalyzed by SARS-CoV-2, EV-71, and HRV-16 RdRp (bottom). Following GS-443902, an intermediate product forms at position 9 (“i + 3”), which is overcome at elevated CTP and UTP concentrations. A 5′-32P-labeled 4-nt primer serves as a size marker. Product formation at and above the asterisk indicates RNA products that are likely a result of sequence-dependent slippage events. EV-71, enterovirus 71; HRV, human rhinovirus; Nsp12, nonstructural protein 12; PDB, Protein Data Bank; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.