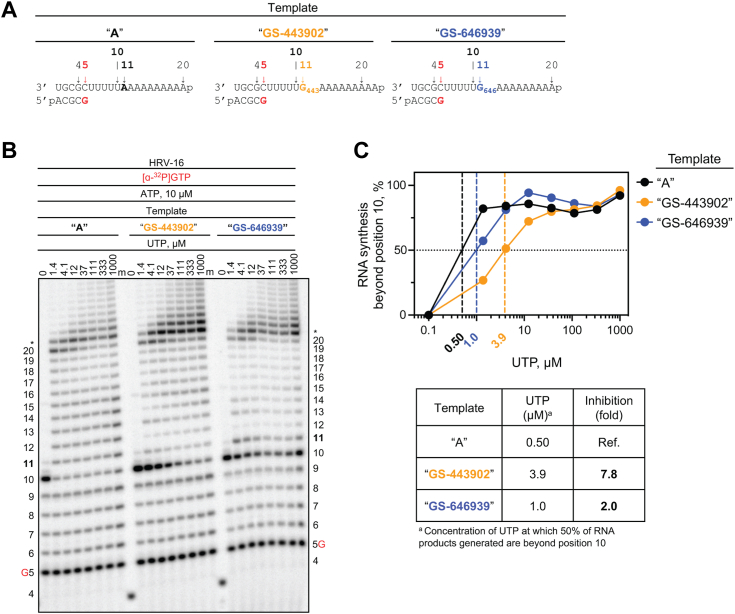
Figure 8.
RNA synthesis catalyzed by HRV-16 RdRp using a template with a single GS-443902 or GS-646939 residue embedded in the template at position 11. A, RNA primer/template with an embedded GS-443902 (Template “GS-443902”, middle) or GS-646939 (Template “GS-646939”, right); the corresponding primer/template with adenosine (Template A) at this position is shown on the left. G5 indicates incorporation of [α-32P]-GTP at position 5. B, migration pattern of the products of RNA synthesis catalyzed by HRV-16 RdRp. MgCl2, [α-32P]-GTP, and ATP provided to the reaction to support RNA synthesis up to position 10. Increasing concentrations of UTP were supplemented to the reactions to monitor incorporation opposite a templated adenosine, GS-443902, or GS-646939 at position 11, and templated adenosines from position 12 to 20. Compared to Template A, intermediate products form at position 10 on Template “GS-443902” and “GS-646939”, indicating template-dependent inhibition. Product formation at and beyond the asterisk indicates RNA products that are likely a result of sequence-dependent slippage events. A 5′-32P-labeled 4-nt primer serves as a size marker. C, quantification of B (top) where the sum of RNA products generated beyond position 10 was divided by the total signal in the lane and normalized as a percentage, fold-inhibition resulting from an embedded GS-443902 or GS-646939 (bottom). To account for template-dependent differences in activity, product fraction was normalized as a percentage to product fraction observed at 1000 μM UTP for that template. HRV, human rhinovirus; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.